MySQL Record display in JTable
Create one Project > give name MYSQL_data_display_JTable
As we will be connecting to MySQL database , so we need to add mysql-connector.jar to connect to MySQL database. We will keep our MySQL data management code in a class my_mysal.java. Inside this class there is a method my_db_select() to collect records from MySQL table. This method my_db_select() will return an array with 4 rows of data and each having 5 columns. So we will declar one 2-D array first.
String[][] data = new String[4][5]; // [rows][columns]SELECT * FROM STUDENT LIMIT 0,4We will loop through this record set to store each row data in our 2-D array data.
int i=0;
while(rs.next()) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
//System.out.print(rs.getString(j+1));
data[i][j]=rs.getString(j+1);
}
//System.out.println();
i=i+1;
}return data;Now we will create one object of class my_mysql.java to access the object my_db_select() to get the data.
String[] column= {"ID","Name","Class","Mark","Sex"};
my_mysql obj=new my_mysql(); // Object is created
//Collect the data using the object obj.my_db_select() with column
jt1 = new javax.swing.JTable(obj.my_db_select(),column);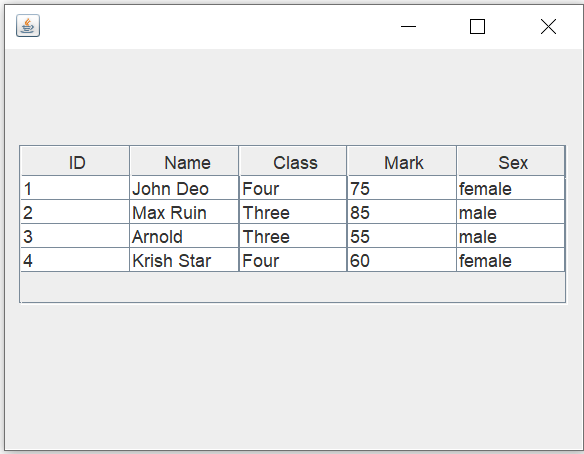
JTable.java
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.border.EmptyBorder;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
public class JTable extends JFrame {
private JPanel contentPane;
private javax.swing.JTable jt1;
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
JTable frame = new JTable();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public JTable() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 400, 305);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
scrollPane.setBounds(10, 64, 366, 107);
contentPane.add(scrollPane);
//My_test obj=new My_test();// with test data
my_mysql obj=new my_mysql();
String[] column= {"ID","Name","Class","Mark","Sex"};
//jt1=new javax.swing.JTable(obj.my_test_select(),column);//test data
jt1 = new javax.swing.JTable(obj.my_db_select(),column);
scrollPane.setViewportView(jt1);
}
}my_mysql.java
import java.sql.*;
public class my_mysql {
public String[][] my_db_select() {
////////////
String[][] data = new String[4][5]; // [rows][columns]
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_tutorial","root","test");
Statement st=con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM STUDENT LIMIT 0,4");
// Looping to store result in returning array data //
int i=0;
while(rs.next()) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
//System.out.print(rs.getString(j+1));
data[i][j]=rs.getString(j+1);
}
//System.out.println();
i=i+1;
}
// Below lines to check data before returning. //
/*
for (int x=0;x<data.length;x++) {
for (int y=0;(data[x]!= null && y <data[x].length);y++) {
System.out.print(data[x][y] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
*/
con.close();
}catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e);}
//////////////////////////////
return data;
}
}download
Download the Java Files here ( right click and save link as to download files ) .JTable.java my_mysql.java My_test.java
swing
Java
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
