Pointers in C
At the time of initialization value of pointer is null and its value is 0.
We can subtract two pointers to find out how many elements are available but we can’t add , multiply or divide pointers
Declaration of Pointers
A double pointer can hold address of a double variable only, it can’t hold address of an integer. We can declare different data type pointers.int *poti; // integer pointer
float *potf; // float pointer
double *potd; // double pointer
char *potch; // Char pointer int f1=3;
potf=&f1; // Storing the address of f1 unary operators
& => Address Of operator
* => Value Of operator
* => Value Of operator
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
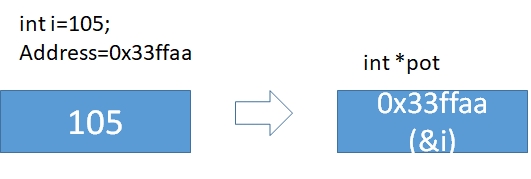
int i=105;
int *pot; // Pointer of an integer //
pot=&i; // assign address of i to pot //
printf(" pot=%d \n *pot= %d, \n i=%d", pot, *pot, i);
return 0;
} pot=6487572
*pot= 105,
i=105Assign data by using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int *pot,i=5;
pot=&i; // Assign address of i to pointr variable pot
*pot=100;// Assigning value of i by using pointer
printf("i value is : %d ",i);
}i value is : 100Understanding difference between pointer and normal variable
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int i=3;
int *pot; // Pointer of an integer //
pot=&i; // assign address of i to pot //
printf(" pot=%d \n *pot= %d, \n i=%d", pot, *pot,i);
return 0;
}pot=6356744
*pot= 3,
i=3#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void){
int u=3;
int v;
int *pu; // Pointer of an integer //
int *pv; // POinter of an integer //
pu=&u; // assign address of u to pv //
v=*pu; // assign value of u to v //
pv= &v; // assign address of v to pv //
printf("\n u=%d &u=%X pu=%X *pu=%d", u,&u,pu,*pu);
printf("\n\n v=%d &v=%X pv=%X *pv=%d",v,&v,pv,*pv);
return 0;
} u=3 &u=60FF04 pu=60FF04 *pu=3
v=3 &v=60FF00 pv=60FF00 *pv=3Add two numbers by using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int *pot1,*pot2,sum, num1,num2;
num1=100;
num2=200;
pot1=&num1;
pot2=&num2;
sum= *pot1 + * pot2;
printf("sum =%d ",sum);
return 0;
}sum =300Swap two numbers by using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int num1=5,num2=10,temp=0;
temp=num2;
int *pot1, *pot2;
pot1=&num1;
pot2=&num2;
temp=*pot1;
*pot1=*pot2;
*pot2=temp; // This is same as num2=temp;
printf("num1=%d , num2=%d",num1,num2);
}num1=10 , num2=5Instead of variable pass pointer as parameter to a function.
Use one function to return final salary after an increase of 15%#include <stdio.h>
int salary(int *basic){
int final_sal=0;
final_sal=*basic*1.5;
return final_sal;
}
int main(void){
int *pot, sal,final_sal;
sal=1000;
pot=&sal;
final_sal=salary(pot);
printf("Final Salary =%d ",final_sal);
}Final Salary =1500Pointer to an array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
int i,num1[5]={3,4,5,6,7};
int *pot; // Pointer of an integer //
pot=&num1; // assign address of num to pot //
for(i=0;i<5;i++){
printf("value : %d : ", num1[i]);
printf("address : %d : ", pot);
printf("\n");
pot++;
}
}value : 3 : address : 6356724 :
value : 4 : address : 6356728 :
value : 5 : address : 6356732 :
value : 6 : address : 6356736 :
value : 7 : address : 6356740 :Passing Pointer of an array as parameter to function
#include <stdio.h>
int array_sum(int *pot){
int k,sum=0;
for(k=0;k<5;k++){
sum = sum+ *pot;
pot++;
}
//sum=ar[2];
return sum;
}
int main(void){
int j[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int sum;
int *pot;
pot=&j[0];
sum=array_sum(pot);
printf("Sum = %d \n",sum);
return 0;
}Sum = 15Char pointer
String is a collection of chars with a null value at the end. Or it is an array of chars.#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
char *potch; // Char pointer
char str[10]="plus2net"; // char array to store string data
potch=&str; // Address of first element of the string.
while(*potch != '\0'){
printf("%c",*potch);
potch++;
}
return 0;
}plus2netPractice Questions on Pointers
- Display the address of an integer variable and one float variable.
- Declare a long variable and store its address in a pointer
- Declare a string variable and store its address in a pointer
- Find sum of two numbers using pointers
- Take two user input numbers and swap them using pointer and display.
- Pass two numbers to a function using pointer and display highest value.
- Create one array and pass the array to a function by using pointer and then display all elements.
- In above question increase the value of elements by 2 inside the function and then display.
- Display highest and lowest numbers in an array using pointer.
- Sort an array using pointers
- Write a program to print a string in revers using pointer
- Print the middle char of a string, if there are even numbers of chars then print the next char from the middle.
- Create a function to receive an pointer of an array and a number to search. This function will return 1 if the number is found inside the array otherwise return 0.
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
