atanh()
import math
print(math.atanh(-0.9)) # -1.4722194895832204
print(math.atanh(0)) # 0.0
print(math.atanh(0.9)) # 1.4722194895832204less than or equal to -1 or more than equal to 1 , we will get ValueError
import math
print(math.atanh(1.0)) Inputs in degree
We can convert radian value to degree and use the sameimport math
in_degree = 50
in_redian = math.radians(in_degree)
print(math.atanh(in_redian)) # 1.3441466416360031.344146641636003 1 radian = 57.2957914331 degree
1 degree = 0.0174533 radian
1 degree = 0.0174533 radian
Drawing graph of atanh()
We will use Matplotlib to generate graph of atanh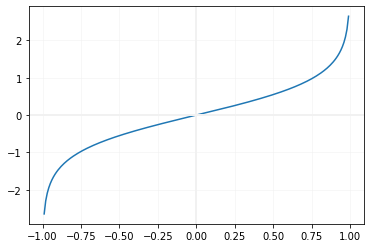
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x=[]
y=[]
i=-0.99
while (i<1):
x.append(i)
y.append(math.atanh(i))
i=i+0.01
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.axvline(x=0.00,linewidth=2, color='#f1f1f1')
plt.axhline(y=0.00,linewidth=2, color='#f1f1f1')
plt.grid(linestyle='-',
linewidth=0.5,color='#f1f1f1')
plt.show()Example 1: Handling Out of Range Values
import math
try:
print(math.atanh(1.5)) # Raises ValueError
except ValueError as e:
print(e)math domain errorExample 2: Using atanh() in Engineering Calculations
import math
signal = 0.5 # A signal amplitude example
result = math.atanh(signal)
print(result) # Output: 0.5493061443340548
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials