Understanding Tkinter: Python's Gateway to GUI Development

Monitor System Resources with Tkinter & psutil
Learn how to use ttkbootstrap and psutil to display real-time CPU, RAM, and disk usage in a stylish Tkinter meter widget.
Read TutorialShow Table of Content
- How to install Tkinter Module
- What is my Tkinter Installed Version?
- check tkinter installation
- Show one blank window.
- geometry()
- What is mainloop() ?
- Change the background colour
- List of widgets in Tkinter
- ttk : Tkinter Themed widgets
- Layout of widgets in Tkinter window
- Handy Reference
- ttkbootstrap
- Tkinter and Database integration
- Dynamic Graphs in Tkinter GUI
- Transparent Window
- Time delay using after()
- Creating windows EXE file from Tkinter
- important tips for application development
- Project : GUI Text Editor
- QR code generator

Tkinter, an integral part of Python's standard library, is a powerful tool for crafting graphical user interfaces (GUIs). This library equips developers with an array of widgets and tools necessary for building robust desktop applications, ensuring seamless functionality across various platforms like Windows, macOS, and Linux. Rooted in the Tk GUI toolkit, originally designed for the Tcl programming language, Tkinter has been adeptly adapted for Python, enhancing its versatility.

How to install Tkinter Module 🔝
Tkinter comes with Python and while installing Python, ensure the Tcl/Tk and IDLE checkboxes are selected. To install Tkinter subsequently we have to use the command like this .C:\Users\user name>pip install tkIf you encounter the error ModuleNotFoundError... no module named 'tkinter' then use the above steps to install Tkinter library.
What is my Tkinter Installed Version? 🔝
import tkinter
print(tkinter.TkVersion) # 8.6 check tkinter installation 🔝
Run this command at your command prompt ( type cmd in your system.)One small window will open showing you the details.
C:\Users\user name>python -m tkinter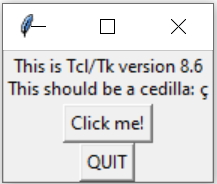
Show one blank window. 🔝
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("500x500") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openmy_w.bind('<Escape>', lambda e:my_w.quit()) # to close. my_w.destroy() Close the window
geometry() 🔝
my_w.geometry("400x350+410+100") # Size & Position350 : Height of the window
410 : Position (opening ) of the window from left or X position
100 : Position (opening ) of the window from Top or Y position
Using height and width variables with geometry of the window. Inside our script we can use these variables.
width,height=710,710 # set the variables
d=str(width)+"x"+str(height)
my_w.geometry(d) my_w.resizable(width=0,height=0) # resizing of window is not allowed my_w.state('zoomed') # default is 'normal' What is mainloop() ? 🔝
The mainloop() function is what keeps a Tkinter application running and responsive. It's the heart of any Tkinter application, it handles events, user interactions, and rendering updates to the GUI. Without calling mainloop(), a Tkinter application would open a window and immediately close it, or not open it at all, since the program would reach its end without waiting for user interaction.Check the two print commands here, after closing of the Tkinter window the last line will be printed. The line just before the last print command my_w.mainloop() will make the program wait for user interactions and will allow further execution ( below it ) once the window is closed.
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk() # root window
my_w.geometry("400x250") # Size of the window
print( ' I am before mainloop ')
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window open
print(' I am after mainloop')Change the background colour 🔝
my_w.configure(background='black')
#OR
#my_w.configure(background='#FFFF00')List of widgets in Tkinter 🔝
Basic Widgets
- Button: Add button with click events and style
- Label: Add Label and change text & other attributes
- Entry: Add Text box, Single line text entry
- Text: Add Text box, Multi line text entry
- Checkbutton: Read data and manage (set or get) of a checkbutton
- Radiobutton: Read data and manage (set or get) of a Radio button
Container and Layout Widgets
- frame: Group widgets and add separator to window
- LabelFrame: Group Widgets and add Label
- PanedWindow: Container allowing user to adjust the size by using the mouse
- Toplevel: Display pop-up or child window from Parent
Selection and Input Widgets
- Listbox: Read selection, add elements to a listbox
- OptionMenu: Drop down box to select one of many options
- Spinbox: User selection from a range of options
- Scale: Use slider to fix value
- StringVar: tk.StringVar() and trace with callback functions
Menu and Dialog Widgets
- Menu: Menu with option and methods
- Menubutton: Dropdown menu
- MessageBox: Show Message box and take user choice
- askopenfile: Dialog box to show file browser & upload file from local system
- askopenfile: Upload and display images using file browser
- colorchooser: Access the native colour picker dialog
- simpledialog: Dialog box to take user input
Visual and Drawing Widgets
- Canvas: Draw Line, Arc, Oval, Polygon, rectangle etc
- image: Displaying icon and Images on Window
- Scrollbar: Scrollbar options and uses
Special Purpose Widgets
- Message: Displaying in-process Messages
- DateEntry: Display Drop-down Date entry
- clock: Display time with Date
- Calendar: Display Date picker
- colors: Tkinter supported colors list
ttk : Tkinter Themed widgets 🔝
ttk, which stands for Themed Tk, is a newer addition to Tkinter that provides access to the themed widget set introduced in Tk 8.5. This module allows for the creation of widgets that can more closely match the native look and feel of a user's operating system.import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttkButton, Checkbutton, Entry, Frame, Label, LabelFrame, Menubutton, PanedWindow, Radiobutton, Scale, Scrollbar, and Spinbox.
The other six are new:
| Combobox | Managing options of a dropdown Combobox |
| Notebook | Methods and options to manage Tabs |
| Progressbar | Displaying status of process with options and methods |
| Separator | Vertical and Horizontal separators |
| Sizegrip | Adding window resizing capabilities. |
| Treeview | Basics of Treeview for tabular data |
Layout of widgets in Tkinter window 🔝
| grid | Organizes widgets in rows and columns, offering more precise control. |
| pack | Simple, arranges widgets in blocks either vertically or horizontally. |
| place | Places widgets at exact x, y coordinates for precise positioning. |
Handy Reference 🔝
| Attributes | How to list, read or update the values |
| validation | Validating user inputs |
| Events | Mouse and Keyboard Events using Call back functions |
| config() | access the access the object's attributes after its initialization |
| clipboard() | Copy and Paste data from Tkinter |
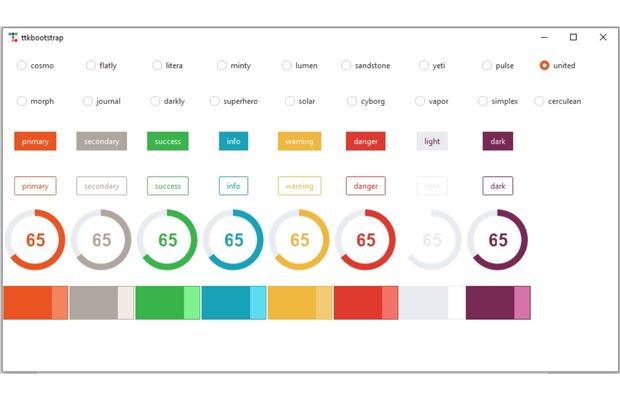
ttkbootstrap 🔝
Tkinter and Database integration 🔝

Tkinter and MySQL Integration
Learn how to connect your Tkinter applications to MySQL databases. Manage records, display data using Treeview, and implement features like search, pagination, and CRUD operations.
Explore MySQL TutorialsTkinter and SQLite Integration
Discover how to integrate Tkinter with SQLite for lightweight and efficient database management. Learn to create tables, insert, update, and fetch data directly within your GUI applications.
Explore SQLite Tutorials| Exercise | Exercise on Tkinter and Managing MySQL database |
Dynamic Graphs in Tkinter GUI 🔝
Display Pandas DataFrame graphs in TkinterTo list all available methods of any widget
l3 = tk.Label(my_w, text='Welcome')
object_methods=[l3 for l3 in dir(tk.Label)
if callable(getattr(tk.Label,l3))]
print(object_methods)Download .zip file with .ipynb files
of Video Tutorials
Transparent Window 🔝
my_w.attributes('-alpha',0.5)Time delay using after() 🔝
l1 is one Label, this code will update the text on Label l1 after 3000 millseconds ( 3 seconds ).l1.after(3000,lambda:l1.config(fg='white',bg='white',text=''))Difference between sleep() and after()
In Tkinter,time.sleep(1) blocks the entire UI, freezing the application and making it unresponsive until the sleep period ends. This prevents Tkinter from processing events like button clicks or window closing, often leading to errors if the user closes the app during execution. On the other hand, after(1000, function) schedules a function to run after a delay without blocking the main event loop, keeping the UI responsive. This makes after() the preferred choice for animations, countdowns, and periodic updates in Tkinter applications.
Creating windows EXE file from Tkinter 🔝
From command prompt move to the directory where your source file is there ( this is required if path is not set ) . You can run from your existing prompt also.
python3 -m PyIntaller tk-clock.pyApplication development by using PyInstaller
important tips for application development 🔝
Don’t initialize any widgets inside a function. Start them from root of your script and manage the options (attributes) from inside the functions by using config() method.Keep the common requirements like Database connection string in a common file and call them from different scripts. This helps in changing the login details in one location when you shift to different database.
If you have common logo, background colour etc. then store them inside config.py file ( can use any other name ) and call them from different scripts. Easy maintenance.
Project : GUI Text Editor 🔝
Text Editor with all file handling operations like New, Open., Save, Save As and Close to add or update data of the file.The tkinter filedialog is used to display file handling dialog boxes and Menu is used to execute various functions to manage a file.
Tkinter Text Editor to Manage File Operations
QR code generator 🔝


📘 Free Download: Tkinter Mastery PDF
Dive into the fundamentals and advanced features of building Python GUIs using Tkinter. This PDF guide covers core widgets, data integration techniques, event handling, styling with ttkbootstrap, and hands-on examples like real-time clock, form validation, and database operations. Perfect for developers and students!
Projects using Tkinter Python Tkinter Live Session at 7 PM in Hindi

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials