Numpy mean()
numpy.mean(a,axis=None,dtype=None,out=None,keepdims=False)a | array, elements to get the mean value |
axis | Int (optional ), or tuple, default is None. If axis given then across the axis is returned. |
dtype | data-type( Optional ), Data Type of returned array or value. |
out | Optional. If given then output to be stored. Must be of same time as of the output |
keepdims | Bool ( Optional ), output matches to the input array dimension. |
Sample array
You can use randint() to create an array for our examples. Or can use fixed elements to create the array.import numpy as np
# my_data=np.random.randint(2,high=7,size=(3,3),dtype='int16')
my_data=np.array([[6, 3, 2], [2, 6, 2], [6, 2, 3]])
print(my_data)[[6 3 2]
[2 6 2]
[6 2 3]]Axis
Sum of the elements across the axis.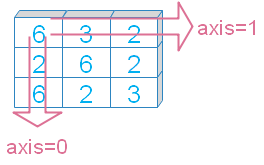
print("mean() : ", my_data.mean())
print("mean(axis=0):", my_data.mean(axis=0))
print("mean(axis=1):", my_data.mean(axis=1))mean() : 3.5555555555555554
mean(axis=0): [4.66666667 3.66666667 2.33333333]
mean(axis=1): [3.66666667 3.33333333 3.66666667]dtype
The data type of the output. By default the output will have the dtype of input array.print("mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int8) : ", my_data.mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int8))
print("mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int32) : ", my_data.mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int32))
print("mean(axis=1,dtype=np.float64) : ", my_data.mean(axis=1,dtype=np.float64))
print("mean(axis=1,dtype=np.complex128) : ", my_data.mean(axis=1,dtype=np.complex128))mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int8) : [3 3 3]
mean(axis=1,dtype=np.int32) : [3 3 3]
mean(axis=1,dtype=np.float64) : [3.66666667 3.33333333 3.66666667]
mean(axis=1,dtype=np.complex128) : [3.66666667+0.j 3.33333333+0.j 3.66666667+0.j]keepdims
If it is set to True ( keepdims=True ) then it will take the dimension of input array.print("mean(keepdims=True) : ", my_data.mean(keepdims=True))
print("mean(keepdims=False) : ", my_data.mean(keepdims=False))mean(keepdims=True) : [[3.55555556]]
mean(keepdims=False) : 3.5555555555555554out
Alternative output array, must be of same shape as expected output. Let us first check with axis.x = np.zeros(3,dtype=int)
print(my_data.mean(axis=0,out=x))
print(x)[4 3 2]
[4 3 2]y = np.array(1)
print(my_data.mean(out=y))
print(y)3
3
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials