Creating Array ()
Creating array
import numpy as np
ar=np.array([1,5,2,8,3])
print(ar) # [1 5 2 8 3]Creating two dimensional array
ar=np.array([[1,5,2,8,3],[8,5,3,11,1]])
print(ar)[[ 1 5 2 8 3]
[ 8 5 3 11 1]]For the two dimensional array we will get this output.
print(ar.shape) # (3, 4)Creating arrays using ones() and eye()
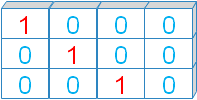 Read more on eye() here.
Read more on eye() here. We can create array by using eye(). We will get an array by filling 1 at diagonal positions.
Let us create one array by (3,4) shape.
ar=np.eye(3,4)
print(ar)[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1. 0.]]ones()
 We can create array of any shape and fill it by 1s by using ones().
We can create array of any shape and fill it by 1s by using ones().
ar=np.ones((4,3))
print(ar)[[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]]Creating array using arange()
Using arange() we can create array with evenly spaced valuesprint(np.arange(1,5,dtype=np.int8)) # [1 2 3 4]Creating array using linspace
Using linespace() we can create array with given number of elementsprint(np.linspace(2,10,5)) # [ 2. 4. 6. 8. 10.]Aray with random numbers
We can create array with random numbersmy_data=np.random.rand(4)
print(my_data)[0.3630618 0.76575666 0.36043609 0.69937788]Array with zeros()
We can create array filled with zeros by using zeros()ar=np.zeros(4,dtype=int)
print(ar) # [0 0 0 0]Using np.full()
We can create array by filling any data by using full()ar=np.full((1,3),5)
print(ar) # [[5 5 5]]Creating empty array
We can create array without initializing entries.ar=np.empty((1,3))
print(ar)[[5.e-324 5.e-324 5.e-324]]Creating Multidimensional array
We will be creating multidimensional arrays by specifying ndim value.ar = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4,5,6], ndmin=2)
print(ar)
print('Shape :', ar.shape)
print('Dimension :',ar.ndim)[[1 2 3 4 5 6]]
Shape : (1, 6)
Dimension : 2Numpy ones() bincount() arange() linspace()

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials