insert() : Adding at given position
We can add values at the given index position of a Numpy array by using append().
numpy.insert(arr,obj, values, axis=None)arr : Values are added to the copy of this array. obj : index or indices before which the value will be added. values : Values to be added to arr. Must be of same shape of the arr ( if Axis is present ). If Axis is not specified then matching shape of arr is not prerequisite. axis : (Optional) Direction in which the values to be appended. Arrays are flattened before insert() if axis is not given.
Note that there is no change to the original array.
import numpy as np
npr=np.array([5,8,3])
npr1=np.insert(npr,1,10) # adding value ( 10 ) at index position 1
print(npr) # [5 8 3] , No change to original array
print(npr1)# [ 5 10 8 3], element added at 2nd position import numpy as np
npr=np.array([5,8,3])
npr1=np.insert(npr,len(npr),10) # adding at the end
print(npr) # [5 8 3] , No change to original array
print(npr1) # [ 5 8 3 10] , 10 added at the endUsing 2-D array
if Axis is provided then adding array or values must have same shape of the original array. In case of any mismatch we will get this error message.ValueError: could not broadcast input array from shape (1,5) into shape (1,4)
import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
#npr1=np.insert(npr,1,[10,11,12,13,14],axis=0) # valueError
npr1=np.insert(npr,1,[10,11,12,13],axis=0)
print(npr1)[[ 0 1 2 4]
[10 11 12 13]
[ 3 4 5 6]
[ 6 7 8 9]]Using axis
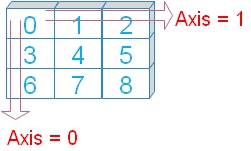 Axis are the directions in rows and columns.
Axis are the directions in rows and columns. Axis 0 is the downward direction or in rows order.
Axis 1 is the horizontal direction or in column order.
import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.insert(npr,1,[10,11,12],axis=1)
print(npr1)[[ 0 10 1 2 4]
[ 3 11 4 5 6]
[ 6 12 7 8 9]]import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.insert(npr,[1,2,3],[10,11,12],axis=1)
print(npr1)[[ 0 10 1 11 2 12 4]
[ 3 10 4 11 5 12 6]
[ 6 10 7 11 8 12 9]]import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.insert(npr,[1,2,3],[99],axis=1)
print(npr1)[[ 0 99 1 99 2 99 4]
[ 3 99 4 99 5 99 6]
[ 6 99 7 99 8 99 9]]import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.insert(npr,[1,2,3],[99],axis=0)
print(npr1)[[ 0 1 2 4]
[99 99 99 99]
[ 3 4 5 6]
[99 99 99 99]
[ 6 7 8 9]
[99 99 99 99]]import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],
[3,4,5,6],
[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.insert(npr,1,[10,11,12])
print(npr1)[ 0 10 11 12 1 2 4 3 4 5 6 6 7 8 9]import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],[3,4,5,6],[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.array([10,11,12,13,21,22,23,24,31,32,34,35]) # different shape
#npr1=npr1.reshape(3,4)
npr1=npr1.reshape(npr.shape) # Match the shape of first array
npr2=np.insert(npr,2,npr1,axis=0)
print(npr2)[[ 0 1 2 4]
[ 3 4 5 6]
[10 11 12 13]
[21 22 23 24]
[31 32 34 35]
[ 6 7 8 9]]Example
Adding one element in each row. Note how the shape is matched.import numpy as np
npr=np.array([[0,1,2,4],[3,4,5,6],[6,7,8,9]])
npr1=np.array([[10],[11],[12]]) # One element for each row
npr2=np.insert(npr,[3,2,1],npr1,axis=1)
print(npr2)[[ 0 10 1 10 2 10 4]
[ 3 11 4 11 5 11 6]
[ 6 12 7 12 8 12 9]]
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials