Pandas DataFrame rolling() — Moving Averages, Windows & Time-Based Operations
DataFrame.rolling(window, min_periods=None,center=False,on=None,
win_type=None, axis=0, closed=None,step=None,method='single')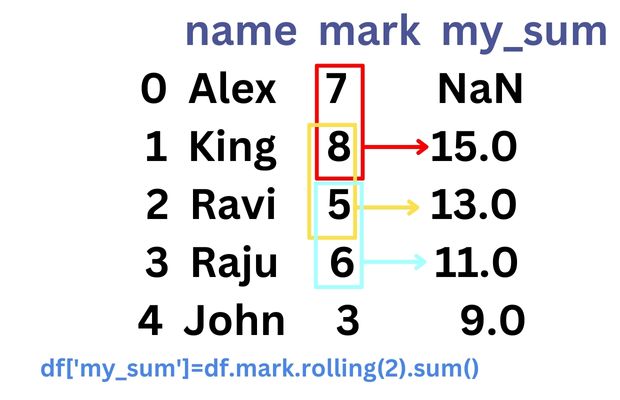
window: Size of the windowmin_periods : Minimum number of observation required to have a value. center Bool, default : False, set the window Label to right edge. win_type : None, If a string, it must be a valid scipy.signal window functionon : a column label or Index level on which to calculate the rolling window. axis : 0 ( defalut ) or 1 , Axis = 0 is across rows, axis = 1 is across columns. closed : None (default), 'right', 'left','both','neither'. Points to exclude from calculation. step : None ( default ), int , Evaluate the window at every step resultmethod : single ( default ) or table, how to execute rolling operation
import pandas as pd
my_dict={
'name':['Alex','King','Ravi','Raju','John'],
'mark':[7,8,5,6,3]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict) # create DataFrame
#print(df.mark.rolling(2).sum()) # rolling window values
df['my_sum']=df.mark.rolling(2).sum() # New column with rolling window values
print(df) name mark my_sum
0 Alex 7 NaN
1 King 8 15.0
2 Ravi 5 13.0
3 Raju 6 11.0
4 John 3 9.0min_periods
In above output you can see the first row value for rolling window ( column my_sum ) is NaN. This is because we need an window of two values ( current and previous one ) to get sum value. We can set the min_periods to 1 to specify window length of 1 if two rows are not available. This will change the value of first row only.df['my_sum']=df.mark.rolling(2,min_periods=1).sum() name mark my_sum
0 Alex 7 7.0
1 King 8 15.0
2 Ravi 5 13.0
3 Raju 6 11.0
4 John 3 9.0on
Here we are calculating mean using the column nameprint(df.rolling(2,on='name').mean()) name mark
0 Alex NaN
1 King 7.5
2 Ravi 6.5
3 Raju 5.5
4 John 4.5axis
axis =0 (default ) roll across the rows.axis =1 roll across the columns.
import pandas as pd
my_dict={
'name':['Alex','King','Ravi','Raju','John'],
'mark':[7,8,5,6,3],
'math':[70,80,50,60,30]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict) # create DataFrame
print(df.rolling(2,axis=1).sum()) mark math
0 NaN 77.0
1 NaN 88.0
2 NaN 55.0
3 NaN 66.0
4 NaN 33.0pandas.errors.DataError: Cannot aggregate non-numeric type: object
import pandas as pd
my_dict={
'name':['Alex','King','Ravi','Raju','John'],
'class1':['One','Two','Three','Four','Five'],
'mark':[7,8,5,6,3],
'math':[70,80,50,60,3]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict) # create DataFrame
df['my_sum']=df.rolling(2).math.sum() # rolling window on math column
print(df) name class1 mark math my_sum
0 Alex One 7 70 NaN
1 King Two 8 80 150.0
2 Ravi Three 5 50 130.0
3 Raju Four 6 60 110.0
4 John Five 3 3 63.0Rolling window using Date
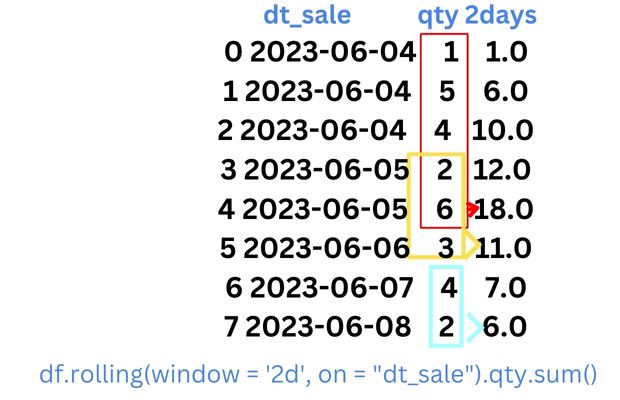
Here more than one record is available in a single day. Here 2 days as considered as window, so multiple rows are used for calculated the values within 2 days rolling.
Here we are using to_datetime() to convert the column to datetime dtype.
import pandas as pd
my_dict={
'dt_sale':['2023-06-04', '2023-06-04',
'2023-06-04', '2023-06-05','2023-06-05','2023-06-06',
'2023-06-07','2023-06-08'],
'qty':[1,5,4,2,6,3,4,2]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict)
df['dt_sale'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dt_sale']) # Cast dtype to datetime
df["2days"] = df.rolling(window = '2d', on = "dt_sale").qty.sum()
print(df) dt_sale qty 2days
0 2023-06-04 1 1.0
1 2023-06-04 5 6.0
2 2023-06-04 4 10.0
3 2023-06-05 2 12.0
4 2023-06-05 6 18.0
5 2023-06-06 3 11.0
6 2023-06-07 4 7.0
7 2023-06-08 2 6.0Using on option on different Date columns
Here we have used two different date columns dt_sale and dt_buy. Two different columns are created by using the windows of these two columns for 2 days.import pandas as pd
my_dict={
'dt_sale':['2023-06-04', '2023-06-04',
'2023-06-04', '2023-06-05','2023-06-05','2023-06-06',
'2023-06-08','2023-06-08'],
'dt_buy' :['2023-06-03', '2023-06-04',
'2023-06-04', '2023-06-05','2023-06-05','2023-06-06',
'2023-06-07','2023-06-08'],
'qty':[1,5,4,2,6,3,4,2]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict)
df['dt_sale'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dt_sale']) # Cast dtype to datetime
df['dt_buy'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dt_buy']) # Cast dtype to datetime
df["2d_sale"] = df.rolling(window = '2d', on = "dt_sale").qty.sum()
df["2d_buy"] = df.rolling(window = '2d', on = "dt_buy").qty.sum()
print(df)
dt_sale dt_buy qty 2d_sale 2d_buy
0 2023-06-04 2023-06-03 1 1.0 1.0
1 2023-06-04 2023-06-04 5 6.0 6.0
2 2023-06-04 2023-06-04 4 10.0 10.0
3 2023-06-05 2023-06-05 2 12.0 11.0
4 2023-06-05 2023-06-05 6 18.0 17.0
5 2023-06-06 2023-06-06 3 11.0 11.0
6 2023-06-08 2023-06-07 4 4.0 7.0
7 2023-06-08 2023-06-08 2 6.0 6.0
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials