SQLite table to DataFrame at Colab platform using read_sql()
read_sql(): Data from SQLite database table to Pandas DataFrame #B06

Inside Colab platform (left side ) use the session drive and upload the sample student excel file.
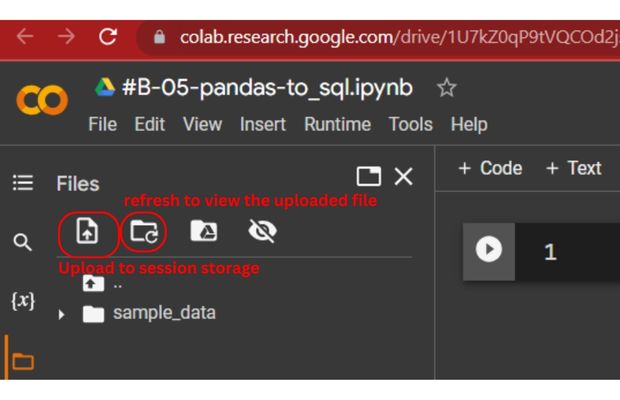
Create the DataFrame using read_excel() and the student Excel file.
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_excel('student.xlsx',index_col='id') # DataFrame created using student file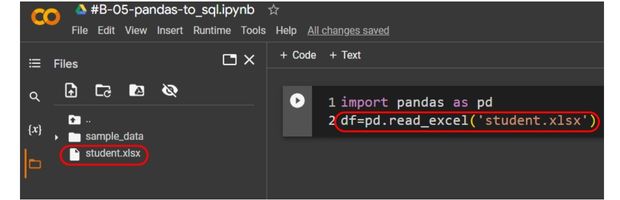
Create the SQlite database and store the same in session drive.
Check the table list from SQLite database
from sqlalchemy import create_engine,text
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
path="sqlite:///my_data.db" # create a SQLite database in google colab session storage
my_conn = create_engine(path)
my_conn=my_conn.connect() # connection is established
try:
result = my_conn.execute(text("select name from sqlite_master where type = 'table'"))
for row in result:
print(row) # Display all tables in SQLite database
except SQLAlchemyError as e:
error = str(e.__dict__['orig'])
print(error) 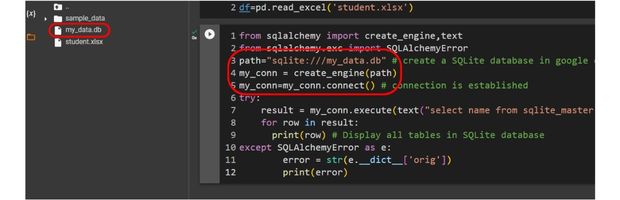
Transfer the DataFrame data to SQLite Database student table by using to_sql().
df.to_sql(con=my_conn,name='student',if_exists='replace') # create student table in sqlite databasetry:
result = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type = 'table'"))
for row in result:
print(row) # List all tables in our SQLite database
except SQLAlchemyError as e:
error = str(e.__dict__['orig'])
print(error) ('student',)result = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM student"))
for row in result:
print(row) # display row from student table. read_sql()
Once our SQLite database is available with the student table ( 35 records ) , we can create our DataFrame using different queries and options.Here we are using all the records of student table and using id column as index.
df=pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM student',my_conn,index_col='id')
print(df) # all rows of data df=pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM student WHERE class="Five"',my_conn,index_col='id')
print(df) # All rows of class = 'Five'q="SELECT * FROM student WHERE class='Five'"
df=pd.read_sql(q,my_conn,index_col='id')
print(df)params
We can pass parameters to the query string separately ( not as a part of the SQL ) by using params option. This is required when inputs are taken from unsecured sources and to prevent injection attack.Here we have declared a place holder inside the query and passing single parameter (
class=Five ) as dictionary.
q="SELECT * FROM student WHERE class=:my_class"
df=pd.read_sql(q,my_conn,index_col='id',params={'my_class':'Five'})q="SELECT * FROM student WHERE class=:my_class AND mark >=:my_mark"
my_dict={'my_class':'Five','my_mark':80}
df=pd.read_sql(q,my_conn,index_col='id',params=my_dict)
print(df)Questions
- How do you use the
read_sql()function in Pandas to read data from a SQL database? - What are the required parameters for the
read_sql()function? - How can you specify a database connection string when using
read_sql()? - Can you pass a custom SQL query to the
read_sql()function? If so, how? - What is the role of the
conparameter in theread_sql()function? - How does
read_sql()handle SQL queries that return multiple result sets? - How can you limit the number of rows fetched from a database using
read_sql()? - Can you provide an example of using
read_sql()with a PostgreSQL database? - What is the default behavior of
read_sql()when encountering NULL values in the database? - How does
read_sql()handle large datasets and memory usage?
Data input and output from Pandas DataFrame Download sample Excel or CSV file or create DataFrame
Pandas DataFrame read_sql (MySQL) read_sql_table insert data

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials