Pickling MySQL table Data & Un-Pickling
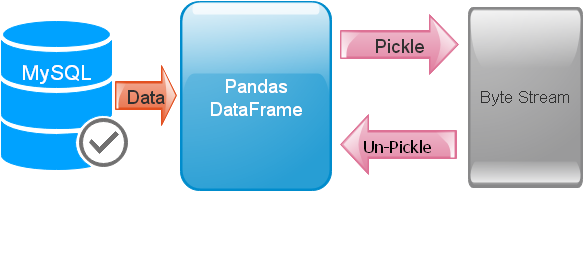
Data stored in MySQL tables can be pickled and un-pickled by using Pandas DataFrame.
What is Pickle .
Here are the steps required for completing the pickling and un- pickling processes.
- Connecting to Database. You can use MySQL connector or SQLAlchemy
- Create a DataFrame by using read_sql()
- Create a file in Binary mode and Pickle the table to this file
import pickle
import mysql.connector
import pandas as pd
my_connect = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="userid",
passwd="****",
database="my_tutorial"
)
####### end of connection ####
my_data = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 0,5",my_connect)
print(my_data) # print output to check
###### end of collecting data and creation of DataFrame #######
fob = open('my_student','wb') # file handling object is created
pickle.dump(my_data,fob) # generated the Pickle
fob.close()Here we have used one SQL Query with LIMIT to get only first 5 records. You can change the query and get different result from MySQL table. We used our Student table in above code.
There is a print command in above code, so 5 records of our student table will be shown ( same as output shown below )
Now we have created the my_student the pickled binary file. Now we will try to read the data by using our un-pickle code.
fob=open('my_student','rb')
my_dict1=pickle.load(fob) # reading the Pickle
fob.close()
print(my_dict1) id name class mark sex
0 1 John Deo Four 75 female
1 2 Max Ruin Three 85 male
2 3 Arnold Three 55 male
3 4 Krish Star Four 60 female
4 5 John Mike Four 60 femaleUsing to_pickle()
In place of using pickle_dump() we can use to_pickle() as we already have the data in Pandas DataFrame and by using this line we can create the file my_student. ( no need to create fob the file object )my_data.to_pickle("my_student")reading pickled data
We can create Pandas DataFrame by using read_pickle() function. We will collect the same ( above ) records by using read_pickle().import pandas as pd
my_dict2=pd.read_pickle('my_student')
print(my_dict2) id name class mark sex
0 1 John Deo Four 75 female
1 2 Max Ruin Three 85 male
2 3 Arnold Three 55 male
3 4 Krish Star Four 60 female
4 5 John Mike Four 60 female
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials