range()
| start | (optional) default = 0 , The start position of the range |
| stop | ( required ), range should Stop before this position |
| step | ( optional ) default =1 , step to consider for the range |
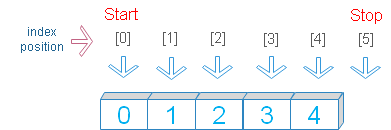
Start, stop and step values are indices of a range.
Python range() function to generate a range of numbers with start stop and step values
If one value is given then it is considered as stop value as default start is 0 and step value is 1.
If two values are given then it is considered as start and stop values and step value is set to 1
If three values are given then they are considered as start , stop and step values.
creating a list using range object
We will create one list by using one range object. Here we have used only stop value. x is the range object.x=range(5) # 5 is stop value
print(list(x)) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]x=range(2,5) # 2 is start ,5 is stop value
print(list(x)) # [2, 3, 4]With start , stop and step values
x=range(2,5,2) # 2 is start ,5 is stop,2 is step value
print(list(x)) # [2, 4]Using a list to create an range
We will create one list whose elements we will use to create one range. We have to unpack the list to get the elements. What is list unpacking ?my_list=[5,40,10]
for i in range(*my_list): # unpacking the list inside range
print(i)5
15
25
35x=range(5,50,10) # range with start=5,stop=50, step=10
my_list=list(x) # list created
print(my_list)[5, 15, 25, 35, 45]Using negative numbers
x=range(5,-10,-3)
print(list(x)) # [5, 2, -1, -4, -7]range data type
By using type()x=range(5) # 5 is stop value
print(type(x)) # <class 'range'>for loop
We used For loop to display elements.for x in range(5):
print(x)0
1
2
3
4
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials