os: Create and delete directories
os.mkdir(path, mode=0o777, *, dir_fd=None)path : Path of the directorymode : Permission leveldir_fd : If dir_fd is not None, it should be a file descriptor referring to a directory, and the path to operate on should be relative; path will then be relative to that directory.
If the directory already exists then we will get this error.
FileExistsError: [WinError 183] Cannot create a file when that file already exists:
If a parent directory in the path does not exist we will get this error.
FileNotFoundError: [WinError 3] The system cannot find the path specified:
Example 1: Create directory
Create one directory in D drive of your system.import os
path='D:\\my_dir'
os.mkdir(path) # create the directory my_dirHere str(i) is used to convert integer to string.
import os
drive='D:\\'
sub_path='my_dir\\'
os.mkdir(drive+sub_path) # create directory D:\my_dir
for i in range(3): # update the level required.
sub_path=sub_path+'my_dir'+str(i)+'\\'
path=drive + sub_path
print(path)
os.mkdir(path)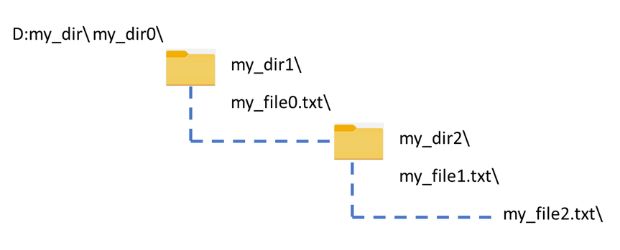
import os
drive='D:\\'
sub_path='my_dir\\'
os.mkdir(drive+sub_path) # create directory D:\my_dir
for i in range(3): # update the level required.
sub_path=sub_path+'my_dir'+str(i)+'\\'
path=drive + sub_path
print(path)
os.mkdir(path)
path_file=path+'my_file'+str(i)+'.txt'
print(path_file)
f = open(path_file, "w") Using try except to catch error
We will use try except error handling to display the error message here.import os
path='D:\\my_dir'
try:
os.mkdir(path) # create the directory my_dir
except (FileExistsError):
print (" File or directory is already exists")
except (FileNotFoundError):
print (" Path is not correct ")
except OSError:
print ("Failed to create %s " % path)
else:
print ("Successfully created the directory %s " % path)makedirs()
By using makedirs() we can make all intermediate-level directories needed to contain the leaf directory.Here None of the directories are existing before and all four directories will be created by using mekedirs()
import os
path='D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3\\my_dir4'
os.makedirs(path) # create all directories in the pathDeleting Directory rmdir()
We can delete the directory if it is empty.import os
path='D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3\\my_dir4'
#os.makedirs(path) # create all directoris in the path
os.rmdir(path) # delete directory my_dir4 listdir()
Listing all the directories and files of a given directory. Here is the code with outputimport os
path='D:\\my_dir\\my_dir0\\my_dir1'
my_list=os.listdir(path)
print(my_list) # ['my_dir2', 'my_file1.txt']Error handling while deleting directories
We will use try except error handling to display the error message while deleting directories.import os
path='D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3\\my_dir4'
#os.makedirs(path) # create all directories in the path
try:
os.rmdir(path) # delete directory my_dir4
except OSError as e:
print(e) # Specific error message
print ("Failed to delete %s " % path)
else:
print ("Successfully deleted the directory %s " % path)[WinError 2] The system cannot find the file specified: 'D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3\\my_dir4'
Failed to delete D:\my_dir1\my_dir2\my_dir3\my_dir4 import os
path='D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3\\my_dir4'
#os.makedirs(path) # create all directories in the path
os.rmdir(path) # delete directory my_dir4 import os
path='D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3'
try:
os.rmdir(path) # delete directory my_dir3
except OSError as e:
print(e) # Specific error message
print ("Failed to delete %s " % path)
else:
print ("Successfully deleted the directory %s " % path)[WinError 145] The directory is not empty: 'D:\\my_dir1\\my_dir2\\my_dir3'
Failed to delete D:\my_dir1\my_dir2\my_dir3 os : operating system interfaces os.walk()

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials