For Loop in Python
for x in range(5):
print(x)
For loop in python to execute code block repeatedly using continue break and else with nested loops
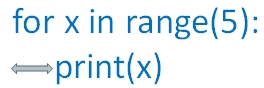 Note that the 2nd line print(x) is placed after an indente of one space. Without that we will get an error asking expectd an indented block . The code to be executed within the block is to be kept with indenting as there is no end of for loop like other languages.
Note that the 2nd line print(x) is placed after an indente of one space. Without that we will get an error asking expectd an indented block . The code to be executed within the block is to be kept with indenting as there is no end of for loop like other languages. The output of above code is here
0
1
2
3
4for x in range(5):
print(x)
print("I am outside the loop")
0
1
2
3
4
I am outside the loopLoop with range
Now we will define a range for the loopfor x in range(5,10):
print(x)5
6
7
8
9for x in range(5,25,5):
print(x)5
10
15
20Break and continue in a for loop
When break statement is encountered the execution comes out of the loop. In case of continue the execution returns to the starting of the loop skipping the rest of the statements ( after continue ) and continues again.In the codes give below , as soon as break is encountered the execution comes out of the loop, so 15 and 20 are not printed. But when continue is used in place of break the printing of 15 is skipped but the loop continues again so 20 is printed.
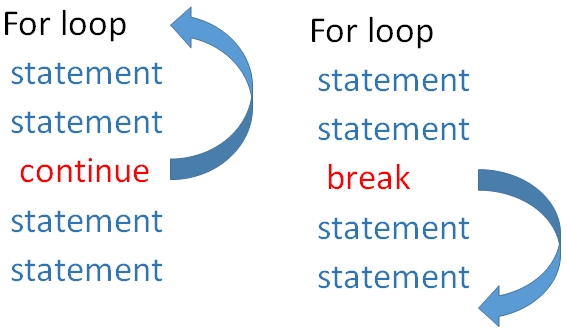
Using continue
for x in range(5,25,5):
if(x==15):
continue
print(x)5
10
20for x in range(5,25,5):
if(x==15):
break
print(x)5
10Using else with for loop
Here else part of the code is executed once the for loop execution is over. However if loop is terminated by using break then else part of the code is skipped.Using continue
for x in range(5,25,5):
if(x==15):
continue
print(x)
else:
print("Out of loop but with else")
print("Out of loop")5
10
20
Out of loop but with else
Out of loopusing break
for x in range(5,25,5):
if(x==15):
break
print(x)
else:
print("Out of loop but with else")
print("Out of loop")5
10
Out of loopnum=100 # change this value to get all prime numbers
for i in range(2,num-1):
for j in range(2,i-1):
if (i%j == 0):
break
else:
print( i," is a prime number")2 is a prime number
3 is a prime number
5 is a prime number
7 is a prime number
-----
-----
83 is a prime number
89 is a prime number
97 is a prime numberUsing list
More on Listnames=["King","Queen","Jack & others"]
for str1 in names:
print(str1)King
Queen
Jack & othersNested for loop
We can keep one for loop inside anotherfor i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
print('*',end='')
print("")*****
*****
*****
*****
*****Using list
names=["King","Queen","Jack & others"]
ages=["child","Young","old"]
for str1 in names:
for str2 in ages:
print(str1,str2)King child
King Young
King old
Queen child
Queen Young
Queen old
Jack & others child
Jack & others Young
Jack & others old
Download the above full source code from Github or run the code in your Google colab platform.
Questions only
https://github.com/plus2net/Python-basics/blob/main/online_class_for_loop_v1.ipynb
Questions only
https://github.com/plus2net/Python-basics/blob/main/online_class_for_loop_v1.ipynb
View and Download for_loop ipynb file ( .html format )


Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com


 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials