Excel to SQLite database and vice versa

We can transfer data from Excel to SQLite database table and from SQLite to Excel by using Pandas DataFrame.
Data Transfer between SQLite and Excel Page using Pandas DataFrame and SQLAlchemy connection
Pandas SQLite
From SQLite to Excel
We will create a Pandas DataFrame by using data from SQLite student table. ( download or create SQLite database with student table)More on Connection to SQLite database
import sqlite3
my_path='G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db' # update path
my_conn = sqlite3.connect(my_path)
print("Connected to database successfully")from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
my_path='G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db' # update path
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///"+ my_path)We are using try except code block to handle errors if any.
Using the Pandas DataFrame df, we will use to_sql() to add the dataframe to Excel sheet.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
my_path='G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db'
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///"+ my_path)
import pandas as pd
try:
query="SELECT * FROM student" # query to collect record
df = pd.read_sql(query,my_conn,index_col='id') # create DataFrame
print(df.head()) # Print top 5 rows as sample
df.to_excel('D:\student.xlsx') # create the excel file
except SQLAlchemyError as e:
#print(e)
error = str(e.__dict__['orig'])
print(error)
else:
print("DataFrame created successfully..")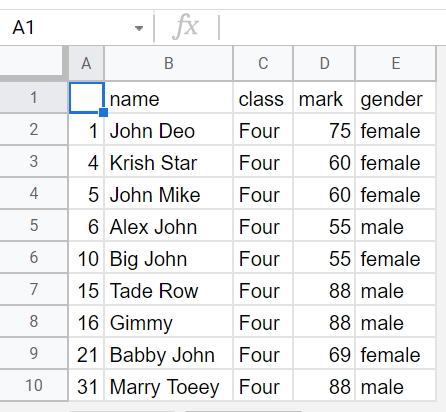
From Excel to SQLite table
In first part by using read_excel() we will collect data from Excel page and create the DataFrame.In second part we will use to_sql() to create and store data from the Dataframe to SQLite table ( student3 table ) .
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
my_path='G:\\My Drive\\testing\\my_db\\my_db.db' # update path
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///"+ my_path) # connection object
import pandas as pd
try:
df = pd.read_excel('D:\\student.xlsx') # create DataFrame by reading Excel
print(df.head()) # Print top 5 rows as sample
df.to_sql(con=my_conn,name='student3',if_exists='append') # create table.
except SQLAlchemyError as e:
#print(e)
error = str(e.__dict__['orig'])
print(error)
else: # show all records to confirm
r_set=my_conn.execute('SELECT * from student3');
for row in r_set:
print(row)From Google sheet to SQLite using Pygsheets and google API authorization From Google sheet to MySQL and vice versa
Database table to Excel file using xlsxwriter

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials