SQLite3 : command line Interface for managing SQLite database files
SQLite3 : command-line tool for managing SQLite database files
We kept the files inside the folder
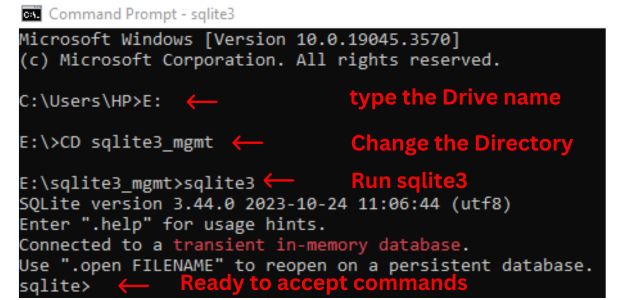
E:\sqlite3_mgmt\. After opening the window command prompt, we navigate to the location and given the command sqlite3.exe or sqlite3 to run the application. You can keep the files in any other location.
How to close the sqlite3 application?
sqlite> .exitsqlite> .helpThis code will create a database file named my_student.db in the specified path if it does not already exist. If the database file already exists, it will be opened instead.
sqlite> .open E:/my_db/my_student.db
sqlite> .tablessqlite> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS
student(id integer primary key,
name text,
class text,
mark integer,
gender text
);sqlite> .tablessqlite> INSERT INTO `student`
(`id`, `name`, `class`, `mark`, `gender`) VALUES
(1, 'John Deo', 'Four', 75, 'female');sqlite> SELECT * FROM student;1|John Deo|Four|75|femalemode 🔝
Get the type of listing by using.mode command.
sqlite> .modesqlite> .mode columnsqlite> SELECT * FROM student;
id name class mark gender
-- -------- ----- ---- ------
1 John Deo Four 75 femalesqlite> .mode insert new_tablesqlite> .mode insert
sqlite> SELECT * FROM student;
INSERT INTO "table"(id,name,class,mark,gender) VALUES(1,'John Deo','Four',75,'female');Let us delete the table
sqlite> DROP table student;Open Database 🔝
Open database and list tables. This will create the database file my_student.db in the given path if it is not there.sqlite> .open E:/my_db/my_student.db
sqlite> .tablessqlite> .conn
ACTIVE 0: E:/sqlite3_mgmt/analytics3.dbSave the database 🔝
sqlite> .save my_student.dbsqlite> .save E:/my_db/my_student.dbCreate the table with 35 records 🔝
Create a new Database my_student2.db and then store 35 records of student tablesqlite> .open E:/my_db/my_student2.dbCREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS
student(id integer primary key,
name text,
class text,
mark integer,
gender text
);
INSERT INTO `student`
(`id`, `name`, `class`, `mark`, `gender`) VALUES
(1, 'John Deo', 'Four', 75, 'female'),
(2, 'Max Ruin', 'Three', 85, 'male'),
(3, 'Arnold', 'Three', 55, 'male'),
(4, 'Krish Star', 'Four', 60, 'female'),
(5, 'John Mike', 'Four', 60, 'female'),
(6, 'Alex John', 'Four', 55, 'male'),
(7, 'My John Rob', 'Five', 78, 'male'),
(8, 'Asruid', 'Five', 85, 'male'),
(9, 'Tes Qry', 'Six', 78, 'male'),
(10, 'Big John', 'Four', 55, 'female'),
(11, 'Ronald', 'Six', 89, 'female'),
(12, 'Recky', 'Six', 94, 'female'),
(13, 'Kty', 'Seven', 88, 'female'),
(14, 'Bigy', 'Seven', 88, 'female'),
(15, 'Tade Row', 'Four', 88, 'male'),
(16, 'Gimmy', 'Four', 88, 'male'),
(17, 'Tumyu', 'Six', 54, 'male'),
(18, 'Honny', 'Five', 75, 'male'),
(19, 'Tinny', 'Nine', 18, 'male'),
(20, 'Jackly', 'Nine', 65, 'female'),
(21, 'Babby John', 'Four', 69, 'female'),
(22, 'Reggid', 'Seven', 55, 'female'),
(23, 'Herod', 'Eight', 79, 'male'),
(24, 'Tiddy Now', 'Seven', 78, 'male'),
(25, 'Giff Tow', 'Seven', 88, 'male'),
(26, 'Crelea', 'Seven', 79, 'male'),
(27, 'Big Nose', 'Three', 81, 'female'),
(28, 'Rojj Base', 'Seven', 86, 'female'),
(29, 'Tess Played', 'Seven', 55, 'male'),
(30, 'Reppy Red', 'Six', 79, 'female'),
(31, 'Marry Toeey', 'Four', 88, 'male'),
(32, 'Binn Rott', 'Seven', 90, 'female'),
(33, 'Kenn Rein', 'Six', 96, 'female'),
(34, 'Gain Toe', 'Seven', 69, 'male'),
(35, 'Rows Noump', 'Six', 88, 'female');Reading Structure of the table 🔝
There are different ways to get the structure of the table. Here invoice_client is our table namesqlite> .schema invoice_clientCREATE TABLE `invoice_client` (
`client_id` integer primary key,
`client_name` text NOT NULL,
`client_add` text ,
`client_state` text,
`client_country` text ,
`client_email` text ,
`client_phone` text
);sqlite> PRAGMA table_info('invoice_client');0|client_id|INTEGER|0||1
1|client_name|TEXT|1||0
2|client_add|TEXT|0||0
3|client_state|TEXT|0||0
4|client_country|TEXT|0||0
5|client_email|TEXT|0||0
6|client_phone|TEXT|0||0sqlite> SELECT sql FROM sqlite_master WHERE tbl_name='invoice_client';CREATE TABLE `invoice_client` (
`client_id` integer primary key,
`client_name` text NOT NULL,
`client_add` text ,
`client_state` text,
`client_country` text ,
`client_email` text ,
`client_phone` text
)Export table to CSV,Excel, Json 🔝
.headers on This will keep the column headers , it can be set to off ( default ) .mode csv Output as csv format .once E:/sqlite3_mgmt/student.csv Output is stored in CSV file at the path given. .system E:/sqlite3_mgmt/student.csv Same as double click on file or opening the file. If path is correct then
.once will create the student.csv file inside the given directory.Let us check this
sqlite> .headers on
sqlite> .mode csv
sqlite> .once E:/sqlite3_mgmt/student.csv
sqlite> SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 0,5;
sqlite> .system E:/sqlite3_mgmt/student.csv
sqlite>In above code change the file type to Excel
sqlite> .excel
sqlite> SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 0,5;
sqlite>Let us create Json file
sqlite> .mode json
sqlite> .once E:/sqlite3_mgmt/student.json
sqlite> SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 10,5;
sqlite>ascii,box,csv,column,html,insert,json,line,
list,markdown,quote,table,tabs,tclImport Data : Create table from CSV file 🔝
We will open our sample database. Here use your location ( path )sqlite>.open E:\sqlite3_mgmt\my_db\my_db.dbsqlite>.tablessqlite> DROP TABLE student;sqlite> .mode csvDownload the sample student CSV file from here.
sqlite> .import D:\my_db\student.csv student1sqlite> .tablessqlite> SELECT * FROM student1;sqlite> .schema student1CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "student1"(
"id" TEXT, "name" TEXT, "class" TEXT, "mark" TEXT,
"gender" TEXT);We can't use the ALTER TABLE statement to modify a column data type in SQLite. Instead we will rename the table, create a new table, and copy the data into the new table.
sqlite> CREATE TABLE student ( id int,name TEXT,class TEXT,mark INT, gender TEXT);sqlite> INSERT INTO student(id,name,class,mark,gender)
SELECT id,name,class, mark,gender FROM student1;sqlite> SELECT * FROM student;sqlite> DROP TABLE student1;Backup and restore database by using dump 🔝
sqlite> .open D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_student.db
sqlite> .output D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_dump.sql
sqlite> .dump
sqlite> .exitsqlite> .read D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_dump.sql
sqlite> .save D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_save.db
sqlite> .exitsqlite> .output D:/sqlite3_mgmt/y22_12.sql
sqlite> .dump y22_12sqlite> .output D:/sqlite3_mgmt/y22_12_str.sql
sqlite> .schema y22_12sqlite> .open D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_save.db
sqlite> .output D:/sqlite3_mgmt/my_all.sql
sqlite> .schemaUsing environmental variable
In my localhost I use SQLite database to store traffic details. This is the string I use to connect to my database..open C:/xampp/htdocs/plus2net/templates/temp1/analytics3.dbsqlite3_changes()
This function is a useful tool for working with SQLite databases. It can be used to verify that queries are executed successfully.SELECT changes()SQLite SQLite3 and PHP

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

