Pandas DataFrame Attributes
| T | Transpose , Changing Columns and indexes |
| at | value at input row , column |
| columns | Name of the Columns as List |
| dtypes | Data types of columns |
| empty | Checking if DataFrame is empty |
| iat | Data at position ( integer based )given as row and column |
| iloc | Data at (label based ) |
| index | Details on row based |
| is_copy | Return the copy ( deprecated) |
| ix | Data based on row and column ( deprecated) |
| loc | Data based on (label based ) Position |
| ndim | Dimension ( axis ) of the DataFrame |
| shape | Number of rows and column as tuple |
| size | Number of elements in DataFrame |
| style | Associated HTML style |
| values | Numpy representation of the DataFrame |
import pandas as pd
print(dir(pd))import pandas as pd
my_dict={'NAME':['Ravi','Raju','Alex','Ron','King','Jack'],
'ID':[1,2,3,4,5,6],'MATH':[30,40,50,60,70,80],'ENGLISH':[20,30,40,50,60,70]}
my_data = pd.DataFrame(data=my_dict)
print(my_data)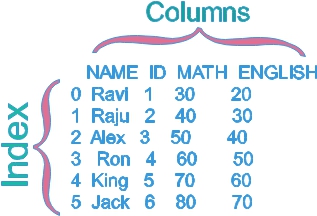 We can print the output here
We can print the output here
NAME ID MATH ENGLISH
0 Ravi 1 30 20
1 Raju 2 40 30
2 Alex 3 50 40
3 Ron 4 60 50
4 King 5 70 60
5 Jack 6 80 70T
T :Transpose , Changing Columns and indexes
print(my_data.T) 0 1 2 3 4 5
NAME Ravi Raju Alex Ron King Jack
ID 1 2 3 4 5 6
MATH 30 40 50 60 70 80
ENGLISH 20 30 40 50 60 70at
at : value at by row, column pair
print(my_data.at[3,'ENGLISH']) # 50 columns
columns: Name of the Columns
print(my_data.columns) Index(['NAME', 'ID', 'MATH', 'ENGLISH'], dtype='object')dtypes
dtypes : dtypes of used DataFrame
print(my_data.dtypes)NAME object
ID int64
MATH int64
ENGLISH int64
dtype: objectempty
empty : The DataFrame empty or not ( True or False )
print(my_data.empty) # False iat
iat : Value at position at rows and columns as integers ( inputs ).
print(my_data.iat[2,3]) # 40iloc
iloc Values at different Positions , More on iloc
index
index : Details on row labels
print(my_data.index) # RangeIndex(start=0, stop=6, step=1)is_copy
is_copy : deprecated
ix
ix : deprecated , position based on row and column
print(my_data.ix[2,'MATH']) # 50 loc
loc : Values , More on loc
ndim
ndim : array dimensions or axes
print(my_data.ndim) #2shape
shape : Tuple giving dimension of DataFrame as ( rows, columns )
print(my_data.shape) # (6,4)size
size : Number of elements in the DataFrame
print(my_data.size) #24Watch the difference between my_data.shape and my_data.size here.
As shape returns the number of rows and columns, we can multiply them to get number of elements which we can also get by using size.
Details on shpe size and ndim
As shape returns the number of rows and columns, we can multiply them to get number of elements which we can also get by using size.
style
style : Associated html style
print(my_data.style)values
values : All values of the DataFrame without axes labels. Numpy representation of the DataFrame.
print(my_data.values)[['Ravi' 1 30 20]
['Raju' 2 40 30]
['Alex' 3 50 40]
['Ron' 4 60 50]
['King' 5 70 60]
['Jack' 6 80 70]]
Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials