Pandas Series
Series can store string, integer and other python objects. It is like one column in a table. Syntax
pandas.Series(data=None, index=None, dtype=None, name=None,
copy=False, fastpath=False)data : array like , iterable , dictionary, list, tuple , scalarindex : have the same length as data, Not necessarily unique,must be a hashable type dtype : Data type of output seriesname: Name given to seriescopy: Default is false, Copy input data
Python Pandas library Series #02
Creating Series
Using List we can create one seriesimport pandas as pd
my_list=['Ravi','Raju','Alex']
s=pd.Series(data=my_list)
print(s)0 Ravi
1 Raju
2 Alexmy_list=['Ravi','Raju','Alex']
my_id=['p','q','r']
s=pd.Series(data=my_list,index=my_id)
print(s)p Ravi
q Raju
r AlexUsing tuple.
my_list=('Ravi','Raju','Alex')
s=pd.Series(data=my_list)
print(s)my_dict={'a':'Ravi','b':'Raju','c':'Alex'}
s=pd.Series(data=my_dict)
print(s)a Ravi
b Raju
c Alexmy_dict={'a':'Ravi','b':'Raju','c':'Alex'}
s=pd.Series(data=my_dict,index=['a','c'])
print(s)a Ravi
c Alex my_dict={'a':'Ravi','b':'Raju','c':'Alex'}
s=pd.Series(data=my_dict,index=['x','y','z'])
print(s)x NaN
y NaN
z NaNs=pd.Series(data='Alex',index=['x','y','z'])
print(s)x Alex
y Alex
z AlexUsing Numpy
We can create one dimensional numpy array.import numpy as np
ar=np.random.rand(4) # Numpy array with random numbers
s=pd.Series(ar)
print(s)From DataFrame to Series
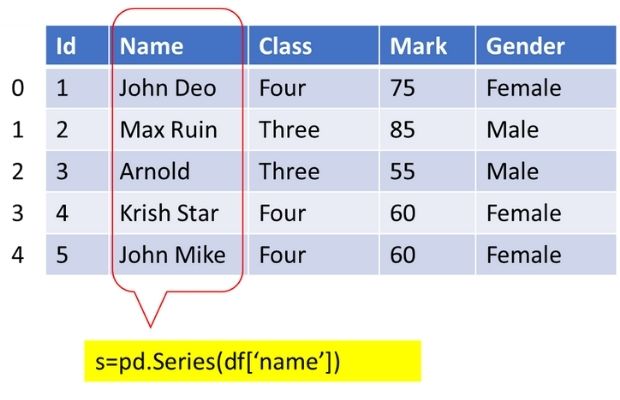
From DataFrame we can create Series by using columns. Read more on our sample student DataFrame. This sample DataFrame has 35 rows.
import pandas as pd
df= pd.read_excel('D:\\my_data\\student.xlsx') # excel file
df= pd.read_csv('D:\\my_data\\student.csv') # csv file
s=pd.Series(df['name']) # using name column data
print(s)s=pd.Series(df.values.tolist())0 [1, John Deo, Four, 75, female]
1 [2, Max Ruin, Three, 85, male]
2 [3, Arnold, Three, 55, male]
3 [4, Krish Star, Four, 60, female]
----
----
31 [32, Binn Rott, Seven, 90, female]
32 [33, Kenn Rein, Six, 96, female]
33 [34, Gain Toe, Seven, 69, male]
34 [35, Rows Noump, Six, 88, female]
Accessing elements of a Series
Using head() and tail() ( above code with 35 records to be used )print(s.head()) # First five records
print(s.head(2)) # last five records
print(s.tail()) # last five records
print(s.tail(2)) # last two records
print(s[:5]) # first 5 recordsprint(s.iloc[3:7]) 3 Krish Star
4 John Mike
5 Alex John
6 My John Robprint(s.iloc[:2].index.tolist()) #List of index of first twoprint(s.iloc[:2].values.tolist()) #List of values of first twoprint(s.iloc[::2]) # alternate rows my_dict={'a':'Ravi','b':'Raju','c':'Alex'}
s=pd.Series(data=my_dict)
print(s['b']) # Output: RajuUpdating elements of series
my_dict={'a':'Ravi','b':'Raju','c':'Alex'}
s=pd.Series(data=my_dict)
s['b']='King' # updating using index
print(s)a Ravi
b King
c AlexConverting Data type of Series
By default this will be inferred from data. Here the id column is integer so by default the dtype is integer (dtype: int64) . Here we have specified the dtype to be string. Check the output by removing dtype='string'. How to create sample student DataFrame?
df= pd.read_csv('D:\\my_data\\student.csv') # csv file
s=pd.Series(df['id'],dtype='string')
print(s) # Name : id , dtype stringimport pandas as pd
l1=[52,13,45,39] # List of values
#l1=['One','Tow','Three','Four'] # List of values
my_id=['x','b','y','p'] # List of index
s=pd.Series(l1,index=my_id) # create a series s=s.apply(lambda x:x+5) # operation on each element print(s.index.tolist()) # List of index print(s['y']) # Key error if not foundprint(s.sum()) # sum of all values / elements print(s.min()) # use max(), mean(),median(),mode()print(s.sort_values()) #print(s.sort_index())s.drop(labels=['b'],inplace=True)s.pop('x') # remove element using keys['z']=50 # adding element using keyprint(s.filter(items=['x','p'])) # searching based on keyprint(s.isin([50,13])) # Matching True or False
#print(s[s.isin([50,13])]) # Matching row only
#print(s[s.isin([50,13])].tolist()) # Matching rows only
#print(s[s.isin([13,39])].index.tolist()) # Matching index or keysto_numpy()
print(s.to_numpy()) # value to Numpy
print(s.index.to_numpy()) # index to Numpy
print(type(s.to_numpy())) # class 'numpy.ndarray'Merging series
import pandas as pd
my_dict1={'a':300,'c':400}
my_dict2={'a':500,'c':200,'d':600}
s1=pd.Series(data=my_dict1)
s2=pd.Series(data=my_dict2)
#s=s1.combine(s2,max,fill_value=0)
s=s1.combine(s2,max)
print(s)a 500.0
c 400.0
d NaN
dtype: float64- How do you create a pandas Series from a list?
- How can you access the index of a Series?
- How do you calculate the sum of values in a Series?
- What method can be used to check if a value exists in a Series?
- How can you change the name of a Series?
- How do you extract the first three elements from a Series?
- What method can be used to sort a Series in descending order?
- How do you apply a mathematical function to each element of a Series?
- How can you find the maximum value in a Series?
- How do you add a new element to a Series?
- Is a Pandas Series one-dimensional?
- Can a Pandas Series contain data of different types?
- Can you perform mathematical operations on a Pandas Series?
- Can you access elements of a Pandas Series by index?
- Can you change the index labels of a Pandas Series?
- Can you add or remove elements from a Pandas Series?
- Can you sort a Pandas Series?
- Can you perform element-wise comparisons on a Pandas Series?
- Can you apply a function to each element of a Pandas Series?
- Can you merge two Pandas Series into a single Series?
- Can you convert a Pandas Series to a NumPy array?
- Can you convert a Pandas Series to a Python list?
- Can you calculate the mean of a Pandas Series?
- Can you calculate the maximum value of a Pandas Series?
- Can you calculate the minimum value of a Pandas Series?
- Can you calculate the sum of all elements in a Pandas Series?
- Can you calculate the standard deviation of a Pandas Series?
- Can you replace specific values in a Pandas Series?
- Can you check if a value exists in a Pandas Series?
- Can you slice a Pandas Series to extract a subset of elements?
contains() to display and delete row based on Conditions

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials