Python tkinter StringVar() trace_add() method
StringVar() in Tkinter is a variable class.
StringVar() is used to track changes to a string value within a Tkinter application.
str1 = tk.StringVar(master,value, name)master: (Optional)The variable is associated with, default value is parent window.value:(Optional) We can set the initial value for the variable. name : (Optional) Name given default is PY_VAR1
Tkitner StringVar() get(), set(), trace_add() methods to manage data and trigger call back functions
trace_add()
trace_add(self, mode, callback)read :Read - the variable is read by someone
write :Write- the variable is written ( updated ) by someone ( frequently used).
unset :undefined – The variable is deleted
or a list or tuple of such strings.
db1.trace_add(['write','read'],my_r) # callback when data read or changesExample of uses of StringVar
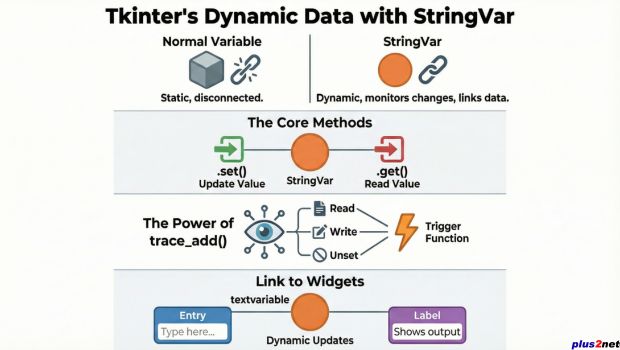
We used one Button and on Click event of this we change the value of the String variable str1 from Hello to Welcome.
b1 = tk.Button(my_w, text='Update', command=lambda: str1.set('Welcome'))trace_add() method is used to attach 'observer' callbacks to the variable
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("300x200") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
def my_r(*args):
print(str1.get()) # Print when variable changes.
str1 = tk.StringVar(my_w) # declare StringVar()
str1.set('Hello')
l3 = tk.Label(my_w, textvariable=str1, width=15)
l3.grid(row=2, column=1)
b1 = tk.Button(
my_w,
text='Update',
command=lambda: str1.set('Welcome')
)
b1.grid(row=2, column=3)
str1.trace_add('write', my_r)
my_w.mainloop()Welcomeset() and get() methods of StringVar
In above examples we used set() method to assign data to the string variable and to read the data stored we used get() method. These two methods are frequently used in our scripts.str1.set('Hello') # assign value to str1
print(str1.get()) # display the value assigned to str1Initializing StringVar
We can using set() method to assign data to StringVar after declaring or we can assign value while declaring the string variable.str1 = tk.StringVar(value='Option 1') # Assign value to str1Resetting StringVar
str1.set("")Length of StringVar
We can use lenlen(str1.get())Normal Variable and StringVar
StringVar() is a class in Tkinter. In a GUI application we require various events to be captured to trigger different functions (requirements). If we use normal Python variable with widgets then monitoring the changes is difficult. However by using a StringVar we can monitor the changes and trigger functions based on the requirements.Example : Declare the password is strong or weak based on the number of chars entered by user. Here we can use StringVar and each time the variable changes its stored data, we can trigger the function checking the length of the input and show the message.
More Examples on StringVar()
The most frequently used method is trace_add(), by using this we can track the changes and trigger function. Here are some scripts using trace_add() method of StringVar().Counting the number of chars
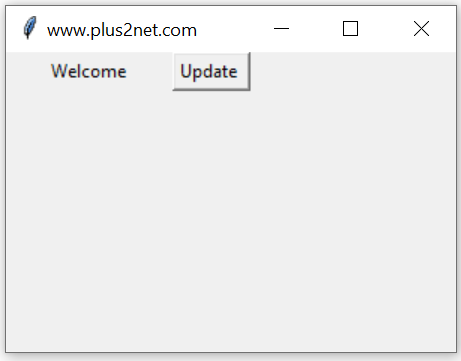
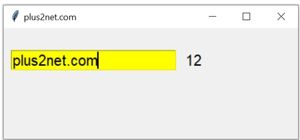 As we enter data inside the entry box, the total number of chars entered will be displayed by the side ( Label l1 ) . Here StringVar() e1_str is connected to Entry widget e1 using textvariable option.
As we enter data inside the entry box, the total number of chars entered will be displayed by the side ( Label l1 ) . Here StringVar() e1_str is connected to Entry widget e1 using textvariable option. The trace_add() method of e1_str is used to trigger the function my_upd() whenever the e1_str data changes.
Inside the function my_upd() we read the user input by using e1.get() , then found out the number of chars by using len() and the converted the integer to string by using str() function.
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x150") # Size of the window width x height
my_w.title("plus2net.com") # Adding a title
e1_str = tk.StringVar() # declaring a StringVar()
e1 = tk.Entry(
my_w,
textvariable=e1_str,
bg='yellow',
font=28
) # Entry box
e1.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=30)
l1 = tk.Label(
my_w,
text='No of Chars here',
font=28
) # added one Label
l1.grid(row=0, column=1)
def my_upd(*args):
l1.config(text=str(len(e1_str.get()))) # read & assign text to StringVar()
e1_str.trace_add('write', my_upd) # triggers on change of StringVar
my_w.mainloop()Try it : Based on the number of chars entered by user, the background color of the entry box should change. Upto 10 chars the Background should be yellow, from 11 to 15 it should be blue and after 15 the background color should change to green.
Updating background color based on number of chars entered
Updating background color based on number of chars entered
Common StringVar() for Entry, Label and Button
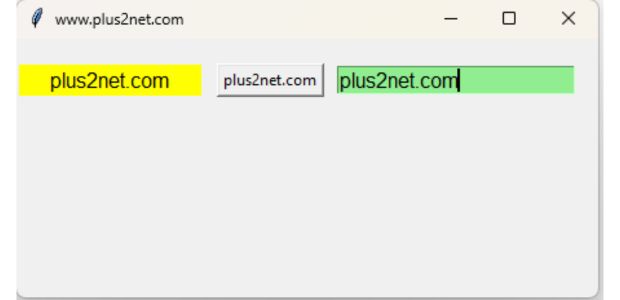
Here we are using one common StringVar() str1 and we are updating text on a Label and Button by using one Entry box. Similarly on Click of a Button the text on Label and inside Entry widgets is also getting updated.
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("450x200") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
def my_r(*args):
print(str1.get()) # Print when variable changes
bt1.config(text=str1.get()) # Update button text
str1 = tk.StringVar(my_w) # Declare StringVar()
str1.set('Hello')
l3 = tk.Label(my_w, textvariable=str1, width=15, font=22, bg='yellow')
l3.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=2, pady=20)
bt1 = tk.Button(my_w, text='Update', command=lambda: str1.set('Welcome'))
bt1.grid(row=2, column=3, padx=10)
e1 = tk.Entry(my_w, textvariable=str1, bg='lightgreen', font=22)
e1.grid(row=2, column=4)
str1.trace_add('write', my_r) # Callback function on write mode
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openUpdating Random text on a Label
We will take random element from a list and display the same on a Label with a time delay.import tkinter as tk
import random
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("300x200") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
str1 = tk.StringVar(value='Randome List') # Using StringVar
my_list = ['King', 'Queen', 'Jack',
'Ronald', 'Ram', 'Tina',
'Vik']
lb1 = tk.Label(my_w, textvariable=str1, width=15, bg='yellow', font=22)
lb1.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=30, pady=50)
def my_fun():
random_element = random.choice(my_list) # Random selection
str1.set(random_element) # Update StringVar
my_w.after(1000, my_fun) # Call the function after a delay
my_fun()
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openUsing Tkinter to Synchronize Entry and Label Widgets with StringVar

This Python program demonstrates how to use the Tkinter library to synchronize an Entry widget with a Label widget using the StringVar() class. The application automatically updates the Label as we type into the Entry widget.
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk() # parent window
my_w.geometry("500x300") # width and height of window
font1 = ["Arial", 22, "normal"] # higher size font
my_str = tk.StringVar() # StringVar for Entry and Label
l1 = tk.Label(my_w, text="Name", font=font1) # added one Label
l1.grid(row=1, column=1)
t1 = tk.Entry(my_w, width=20, bg="yellow",
font=font1, textvariable=my_str) # added one text box
t1.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=10)
l2 = tk.Label(my_w, text="I will update", width=20, bg="lightgreen",
font=font1, textvariable=my_str, anchor="w") # added one Label
l2.grid(row=2, column=2, columnspan=3, padx=10, pady=20)
t1.focus() # Keep the cursor on Entry widget on opening
my_w.mainloop() # to keep the window openTriggering all Modes of StringVar() : an Example
Here we have three buttons, each button triggers one mode ( read, write or unset ) of event associated with StringVar(). Message is printed based on the callback function used.import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("300x100") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
def my_fun():
str2 = tk.StringVar(my_w, value='Welcome2')
print(str2.get())
str2.trace_add('unset', my_unset) # variable is removed
str1 = tk.StringVar(my_w, value='Welcome1')
def my_write(*args):
print(str1.get()) # Print when variable changes
print('write is triggered')
def my_read(*args):
print(str1.get()) # Print when variable accessed
print('read is triggered')
def my_unset(*args):
print('unset is triggered')
bt1 = tk.Button(
my_w,
text='write',
command=lambda: str1.set('plus2net')
)
bt1.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=20, pady=10)
bt2 = tk.Button(
my_w,
text='read',
command=lambda: str1.get()
)
bt2.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=20, pady=10)
bt3 = tk.Button(
my_w,
text='unset',
command=my_fun
)
bt3.grid(row=1, column=3, padx=20, pady=10)
str1.trace_add('write', my_write) # callback when data changes
str1.trace_add('read', my_read) # callback when data read
my_w.mainloop()
Dynamic GUI Updates with StringVar in #Python #Tkinter #PythonGUI | Easy Guide
Questions
- What is the purpose of
StringVar()in Tkinter? - How do you create a
StringVar()object in Tkinter? - Can you explain how
StringVar()is used to link a widget to a variable in Tkinter? - How can you set the initial value of a
StringVar()object? - How do you retrieve the current value stored in a
StringVar()object? - How do you update the value of a
StringVar()object dynamically? - Can you demonstrate how to use
StringVar()to display the value of an Entry widget? - How can you trace changes to a
StringVar()object? - What happens if you try to assign a non-string value to a
StringVar()object? - How do you clear the value stored in a
StringVar()object?
Interlinked Combobbox: how the changes in selection is triggered
DoubleVar() IntVar() BooleanVar()

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

22-03-2021 | |
| Very bad to call a variable in Python "str" str = tk.StringVar(my_w) # declare StringVar() because str is build-in method to stringify data! class str(object='') --> built-in function in Python | |
23-03-2021 | |
| Thanks, Let us use str1 | |
 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials