Task List using Tkinter
Font style
We will use one tuple to create two types of font styles, one for normal and other when task is completed or the checkbox is checked.f_done=('Times',22,'overstrike') # font values to use
f_normal=('Times',22,'normal') # font values to useAssigning the font
Based on the event ( checked or not checked ) we can assign or update the font attribute of the Checkbutton by using config().Attribute fg is used to change the foreground color or font colour of the text.
Once the status of the checkbutton is changed this will trigger the function my_upd().
def my_upd():
if(var.get()==True):
ck.config(font=f_done,fg='green')
else:
ck.config(font=f_normal,fg='blue')
Tkinter Task (todo) list by using Check buttons and managing font overstrike style through events
Full code is here
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x300")
f_done=('Times',22,'overstrike') # font values to use
f_normal=('Times',22,'normal') # font values to use
def my_upd():
if(var.get()==True):
ck.config(font=f_done,fg='green')
else:
ck.config(font=f_normal,fg='blue')
var=tk.BooleanVar() # variable
ck = tk.Checkbutton(my_w, text='My task No :1',
variable=var,onvalue=True,offvalue=False,font=f_normal,fg='blue',
command=lambda: my_upd())
ck.grid(row=0,column=0,padx=10,pady=25)
my_w.mainloop()Dynamic creation of Checkbuttons
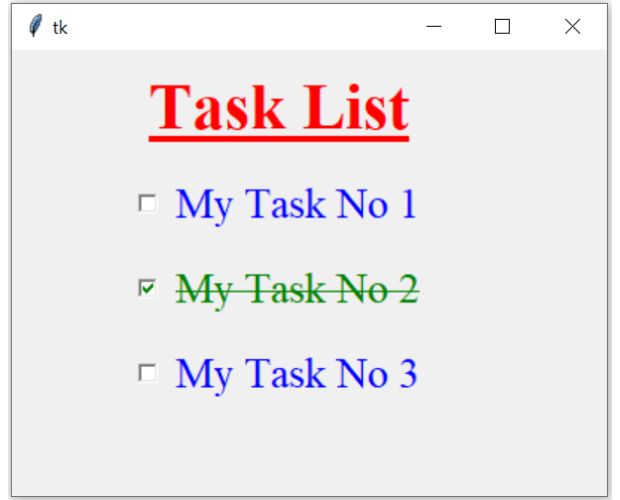
Tkinter task list from Dictionary using key and tasks as values inside a for loop to manage style
We may not be sure about number of check buttons required or number of Tasks we have to display. In this case dynamically we have to create the widgets based on the inputs conditions.
We may have 5 tasks to complete in one day and may have 10 tasks to display in second day.
We used dictionary to store tasks as values with keys.
my_dict={'a':'My Task No 1','b':'My Task No 2','c':'My Task No 3'}my_dict.keys() returns a list of keys and using this inside a for loop, we can create one checkbutton dynamically for each task. Once the status of the checkbutton is changed, the command option calls my_upd(k) by passing the dictionary key k as parameter.
for k in my_dict.keys(): # Number of checkbuttons or tasks
var=tk.BooleanVar() # variable connected to Checkbutton
ck = tk.Checkbutton(my_w, text=my_dict[k],
variable=var,onvalue=True,offvalue=False,font=f_normal,fg='blue',
command=lambda k=k: my_upd(k))
ck.grid(row=i,column=0,padx=80,pady=5,sticky='e') my_ref={} # Storing the references
i=1 # row number ( after using 0 row number for Label at top)
for k in my_dict.keys(): # Number of checkbuttons or tasks
var=tk.BooleanVar() # variable connected to Checkbutton
ck = tk.Checkbutton(my_w, text=my_dict[k],
variable=var,onvalue=True,offvalue=False,font=f_normal,fg='blue',
command=lambda k=k: my_upd(k))
ck.grid(row=i,column=0,padx=80,pady=5,sticky='e')
my_ref[k]=[ck,var] # to hold the references
i=i+1 # increase the row number import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x300")
f_done=('Times',22,'overstrike')
f_normal=('Times',22,'normal')
def my_upd(k): # k is the key of the reference dictionary
if(my_ref[k][1].get()==True): # checkbox is checked
my_ref[k][0].config(font=f_done,fg='green')
else: # Checkbox is unchecked
my_ref[k][0].config(font=f_normal,fg='blue')
l1=tk.Label(my_w,text='Task List',
font=('Times',32,('bold','underline')),fg='red')
l1.grid(row=0,column=0,padx=5,pady=10)
my_dict={'a':'My Task No 1','b':'My Task No 2','c':'My Task No 3'}
my_ref={} # Storing the references
i=1 # row number ( after using 0 row number for Label at top)
for k in my_dict.keys(): # Number of checkbuttons or tasks
var=tk.BooleanVar() # variable connected to Checkbutton
ck = tk.Checkbutton(my_w, text=my_dict[k],
variable=var,onvalue=True,offvalue=False,font=f_normal,fg='blue',
command=lambda k=k: my_upd(k))
ck.grid(row=i,column=0,padx=80,pady=5,sticky='e')
my_ref[k]=[ck,var] # to hold the references
i=i+1 # increase the row number
my_w.mainloop()Using SQLite or MySQL database as source
The list of task with status can be taken from SQLite database and user can update the status of the task by updating the matching column in table.Task list using Database table ( Part III )

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials