start(), step() & stop() methods of Progressbar
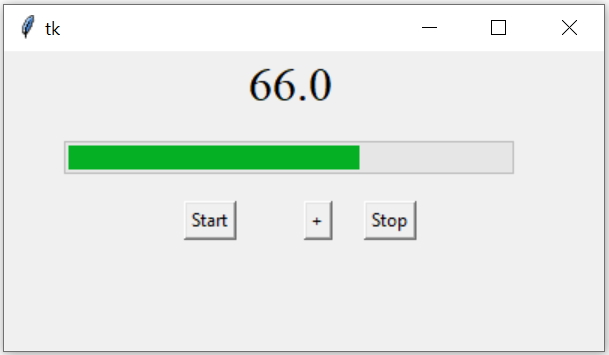
Tkinter Progressbar to show status with options and methods to manage and display values
We used one String Variable x with the variable option of Progress bar. So when the value of the progress bar is changed then the tace() method of string variable executes the my_disp() function to display the value.
The start() method triggers the autoincrement of the progress bar and the step() method increases the value of the progress bar by 10.
The stop() method stops the increment of the progress bar.
Full code is here
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x200")
x=tk.StringVar() # variable of Progressbar
prg1 = ttk.Progressbar(my_w,orient = HORIZONTAL,
length = 300, mode = 'determinate',variable=x)
prg1.place(relx=.1,rely=.3)
b1=tk.Button(my_w,text='Start',command=lambda:prg1.start(500))
b1.place(relx=0.3,rely=0.5)
b2=tk.Button(my_w,text='+',command=lambda:prg1.step(10))
b2.place(relx=0.5,rely=0.5)
b3=tk.Button(my_w,text='Stop',command=lambda:prg1.stop())
b3.place(relx=0.6,rely=0.5)
def my_disp(*args): # display the value at Label
l1.config(text=x.get())
font1=('times',24,'normal')
l1=tk.Label(my_w,textvariable=x.get(),text='value here',font=font1)
l1.place(relx=0.4,rely=0.01)
x.trace('w',my_disp)
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window open| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| start( interval ) | increment the Progress bar in every interval value (50 milliseconds default ) |
| step( amount ) | Default is 1 if omitted, increments in the progress bar value by given amount |
| stop() | Stop the autoincrement mode. |
Progressbar
Options : value, mode ,orient ,variable etc..

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials