Options of Progressbar
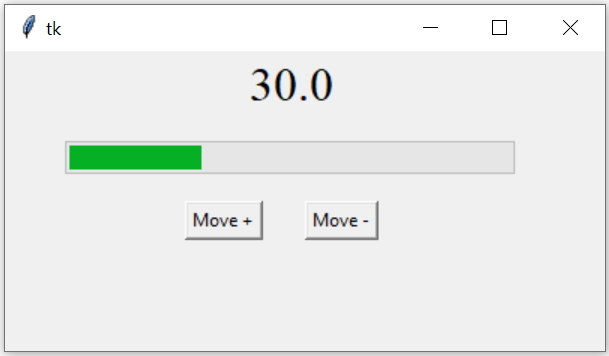
Tkinter Progressbar to show status with options and methods to manage and display values
We used two buttons b1 and b2 to execute our function my_fun() on click event. This function my_fun() receives one parameter whose value is based on which button is clicked.
Inside the function the option value data is incremented or decremented based on the input parameter type and the text option of Label is updated using config().
Full code is here
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x200")
def my_fun(type): # update the value of progress bar
if(type=='+'):
prg1['value'] += 10 # increase value
else:
prg1['value'] -= 10 # decrease value
l1.config(text=str(prg1['value'])) #update Label
prg1 = ttk.Progressbar(my_w,orient = HORIZONTAL,
length = 300, mode = 'determinate')
prg1.place(relx=.1,rely=.3)
b1=tk.Button(my_w,text='Move +',command=lambda: my_fun('+'))
b1.place(relx=0.3,rely=0.5)
b2=tk.Button(my_w,text='Move -',command=lambda: my_fun('-'))
b2.place(relx=0.5,rely=0.5)
font1=('times',24,'normal')
l1=tk.Label(my_w,text='value here',font=font1)
l1.place(relx=0.4,rely=0.01)
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openmode
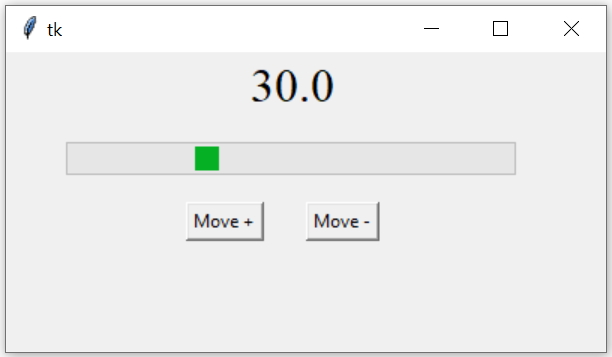
In the above code change the progress bar option mode to indeterminate
prg1 = ttk.Progressbar(my_w,orient = HORIZONTAL,
length = 300, mode = 'indeterminate')Option value and variable
By using value option we can set and read the data of the progress bar. By using vriable option we can connect ( or update ) this data to another variable.Check below how the value of String Variable x is used to display the data in a Label. The data associated with x is taken from the Progress bar by using the option variable
start() step() and stop() Method example
Here is a list of all options of Progressbar
| Options | Details |
|---|---|
| orient | Orientation of the Progress bar. Values are Horizontal or Vertical |
| length | Length of the Progress bar, (width if horizontal, height if vertical) |
| mode | Values can be determinate OR indeterminate Check the examples |
| maximum | Default value is 100, specifies the maximum value. |
| value | The current value of the Progress bar. Can be set or read. |
| variable | Variable can be linked to value of Progress Bar. Realtime changes ( in values ) can be captured. |
Progressbar stopping at maximum and minimum value
In the above code, change the function my_fun() like this by adding conditions. To go beyond 100 the current value must be below 100. Similarly to go below 0 the existing value must be higher than 0.def my_fun(type): # update the value of progress bar
if(type=='+' and prg1['value']<100): # Upper limit is 100
prg1['value'] += 10 # increase value
elif(type=='-' and prg1['value']>0): # Lower limit is 0
prg1['value'] -= 10 # decrease value
l1.config(text=str(prg1['value'])) #update LabelClose the window once the value reached maximum value
def my_fun(type): # update the value of progress bar
if(type=='+' and prg1['value']<100): # Upper limit is 100
prg1['value'] += 10 # increase value
elif(type=='-' and prg1['value']>0): # Lower limit is 0
prg1['value'] -= 10 # decrease value
l1.config(text=str(prg1['value'])) #update Label
if prg1['value']==prg1['maximum']:
my_w.destroy()import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x200")
def my_fun(type): # update the value of progress bar
if(type=='+' and prg1['value']<100): # Upper limit is 100
prg1['value'] += 10 # increase value
elif(type=='-' and prg1['value']>0): # Lower limit is 0
prg1['value'] -= 10 # decrease value
l1.config(text=str(prg1['value'])) #update Label
if prg1['value']==prg1['maximum']:
my_w.destroy()
prg1 = ttk.Progressbar(my_w,orient = HORIZONTAL,
length = 300, mode = 'determinate',maximum=100)
prg1.place(relx=.1,rely=.3)
b1=tk.Button(my_w,text='Move +',command=lambda: my_fun('+'))
b1.place(relx=0.3,rely=0.5)
b2=tk.Button(my_w,text='Move -',command=lambda: my_fun('-'))
b2.place(relx=0.5,rely=0.5)
font1=('times',24,'normal')
l1=tk.Label(my_w,text='value here',font=font1)
l1.place(relx=0.4,rely=0.01)
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openProgressbar
start() step() and stop() Method example

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials