Python tkinter DoubleVar() trace_add()
e_v=tk.DoubleVar(master,value,name)master: (Optional)The variable is associated with, default value is parent window.value:(Optional) We can set the initial value for the variable. name : (Optional) Name given default is PY_VAR1
Tkinter DoubleVar() get(), set(), trace() methods to manage data and trigger call back functions
trace_add()
trace_add(self, mode, callback)read :Read - the variable is read by someone
write :Write- the variable is written ( updated ) by someone ( frequently used).
unset :undefined – The variable is deleted
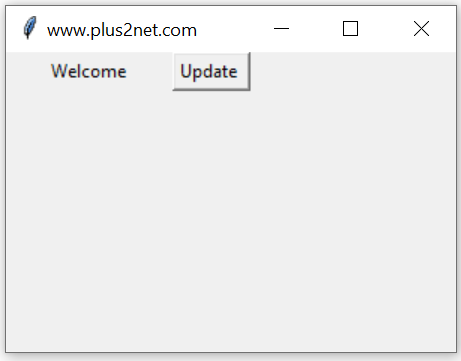
Here is an example which uses w ( write ) mode to display the value of the variable when ever it changes.
We used one Button and used on Click event to change the value of this variable db1 from 5.1 to 10.34.
b1 = tk.Button(my_w,text='Update',command=lambda:db1.set(10.34))trace_add() method is used to attach 'observer' callbacks to the variable
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("300x100") # Size of the window
my_w.title("www.plus2net.com") # Adding a title
def my_r(*args):
print(db1.get()) # Print when variable changes.
db1 = tk.DoubleVar(my_w) # declare DoubleVar()
db1.set(5.1) # assign value to variable
b1 = tk.Button(my_w,text='Update',command=lambda:db1.set(10.34))
b1.grid(row=2,column=3,padx=20,pady=10)
db1.trace_add('write',my_r) # callback when data changes
my_w.mainloop()10.34Use DoubleVar() for handling Float Data
set() and get() methods of DoubleVar
In above examples we used set() method to assign data to the Double variable and to read the data stored we used get() method. These two methods are frequently used in our scripts.db1.set(10.34) # assign value to db1
print(db1.get()) # display the value assigned to db1Initializing DoubleVar
We can using set() method to assign data to DoubleVar after declaring or we can assign value while declaring the string variable.db1=tk.DoubleVar(value=5.1) # Assign value to db1Length of DoubleVar
Before using len function, we have to convert the DoubleVar to string by using str()print(len(str(db1.get())))Normal Variable and DoubleVar
DoubleVar() is a class in Tkinter. In a GUI application we require various events to be captured to trigger different functions (requirements). If we use normal Python variable with widgets then monitoring the changes is difficult. However by using a DoubleVar we can monitor the changes and trigger functions based on the requirements.Example : Calculating division of two numbers or multiplication of user entered decimal numbers requires float variables. Here DoubleVar is used if you want to track the changes in the variable.
Reading Entry box value using DoubleVar
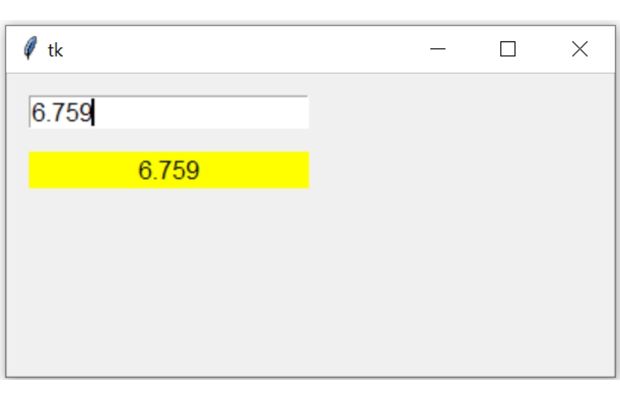
We will connect the variable option of a Entry to BooleanVar() e_v and read the value.
By using trace_add() method of Double variable we will trigger a call back function.
Inside the function we will read the value of Double variable by using get() method and then update the text attribute of a Label by using config() method.
import tkinter as tk
my_w = tk.Tk()
my_w.geometry("400x200") # Size of the window
e_v=tk.DoubleVar() # declare double varible
e_v.set(6.7) # assign the value to Double variable
e1=tk.Entry(my_w,textvariable=e_v,font=20)
e1.grid(row=0,column=0,padx=15,pady=15)
l1=tk.Label(my_w,text='Output',font=22,bg='yellow')
l1.grid(row=1,column=0,padx=15,sticky='ew')
def my_upd(*ags): # call back function
my_data=e_v.get() # reading value of Double var
l1.config(text=str(my_data)) # display in Label
e_v.trace_add('write',my_upd) # track the changes of Double variable
my_upd() # call the function to update the display
my_w.mainloop() # Keep the window openApplication using DoubleVar
For conversion of measurement units like feet to meter and from meter to feet we used DoubleVar.Convert Feet to Meter and vice versa
StringVar() BooleanVar() IntVar()

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials