Meter bootstyle based on Range
Triggering changes in meter value
We kept the optioninteractive=True, so when the value of the meter i.e amountusedvar is changed by mouse, it triggers the function my_upd() by using the trace method.
m1.amountusedvar.trace_add("write", my_upd) # On change of amountusedvar
Bootstyle parameter to manage colour based on amountused value of a Ttkbootstrap Meter widget #7
Function my_upd()
This function is called when the value or amountusedvar option of the meter is changed. Inside this function we will keep if elif condition checks to set the option bootstyle to different colors. There are 8 different colors are already avilable here is the list.PRIMARY, SECONDARY, SUCCESS, INFO, WARNING, DANGER, LIGHT, DARK
def my_upd(*args):
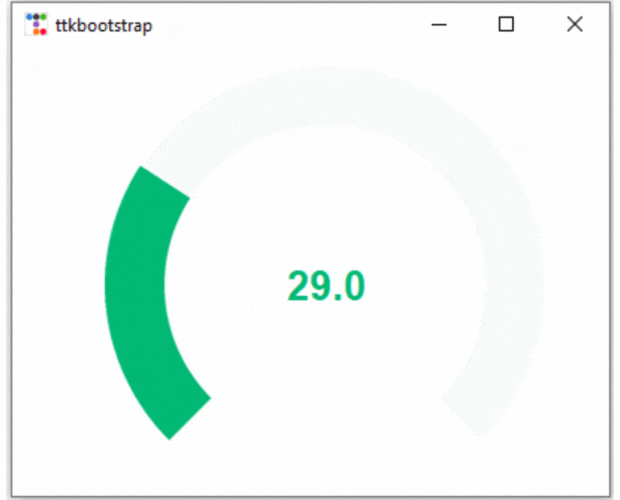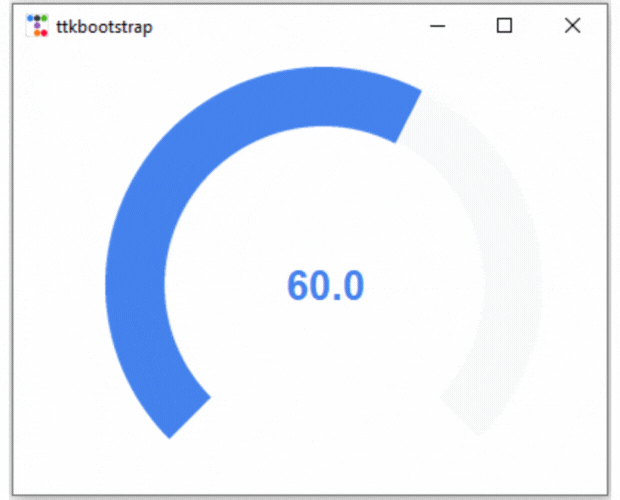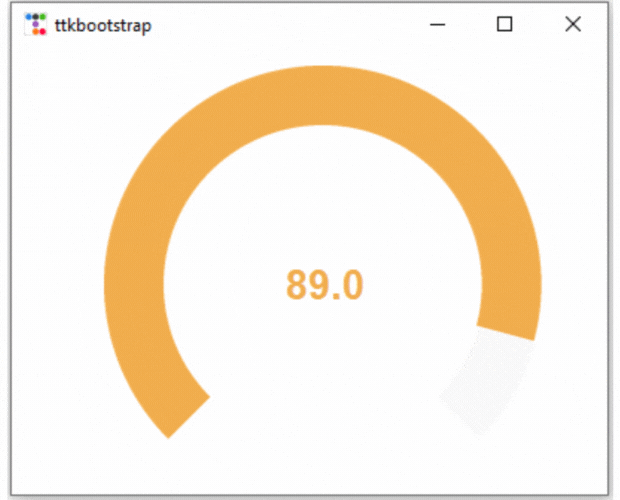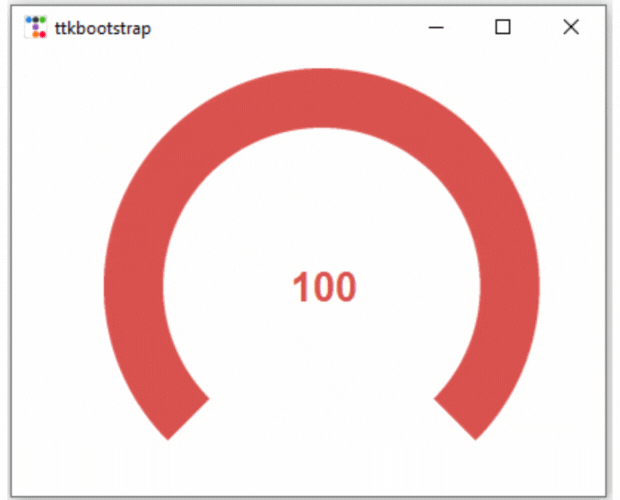
if m1["amountused"] <= 30:
m1["bootstyle"] = SUCCESS
elif m1["amountused"] <= 60:
m1["bootstyle"] = PRIMARY
elif m1["amountused"] <= 90:
m1["bootstyle"] = WARNING
else:
m1["bootstyle"] = DANGER
import ttkbootstrap as ttk
from ttkbootstrap.constants import *
my_w = ttk.Window()
my_w.geometry("400x300")
def my_upd(*args):
if m1["amountused"] <= 30:
m1["bootstyle"] = SUCCESS
elif m1["amountused"] <= 60:
m1["bootstyle"] = PRIMARY
elif m1["amountused"] <= 90:
m1["bootstyle"] = WARNING
else:
m1["bootstyle"] = DANGER
m1 = ttk.Meter(
my_w,
amountused=10,
metersize=300,
meterthickness=40,
interactive=True,
metertype=SEMI,
bootstyle=SUCCESS,
)
m1.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=60, pady=10)
m1.amountusedvar.trace_add("write", my_upd) # On change of amountusedvar
my_w.mainloop()
Ttkbootstrap Meter Displaying number of chars entered in Text widget using Meter
ttkbootstrap
Monitor System Performance using ttkbootstrap Meter and psutil Countdown Timer using ttkbootstrap Meter

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials