Tableview data sources
Ttkbootstrap Tableview using MySQL SQLite CSV Excel and DataFrame as data sources
Sample data from different Data Sources
Sample data in Excel, CSV, MySQL dump, SQLite databae, Pandas DataFrameNumber of columns to display
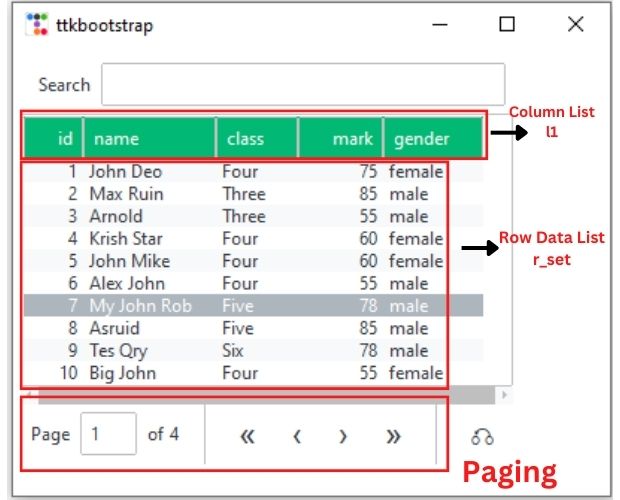
When we collect data from the source ( database table or Excel or CSV file ) we are not sure how many columns will be available. Here are some SQL which collects different number of columns from the table
SELECT id, name FROM student;
SELECT id, name, class FROM student;
SELECT * FROM student;This way we will not have any fixed number of columns and based on the source or data, we have to create the columns.
For our easy understanding let us create one list and use the elements as column headers. We can replace our list with data from Database table.
l1 = ['id', 'Name', 'Class', 'Mark', 'Gender']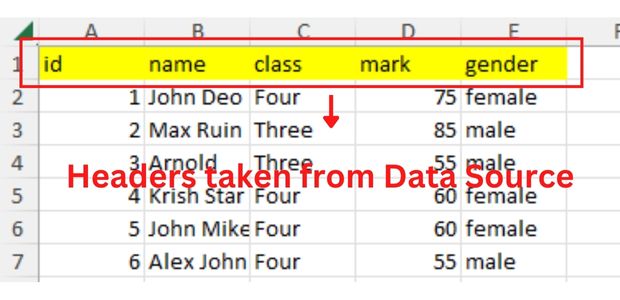
We will replace the list l1 in above code with our data column headers and for that we have used our MySQL table. Note that souce can be SQLite or Excel or Pandas DataFrame or any other source.
Creating the Tableview
dv = ttk.tableview.Tableview(
master=my_w,
paginated=True,
searchable=False,
bootstyle=PRIMARY,
pagesize=10,
height=10,
coldata=l1,
rowdata=r_set,
stripecolor=(colors.light, None),
)
dv.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5) # Tableview is placedWe need to create two variables ( l1 and r_set ) , one is list of headers and other one is list of row data.
Let us work with different data sources. Based on the requirment any part of the code can be un-commented to include as source.
MySQL database table as data source
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
my_conn = create_engine("mysql+mysqldb://userid:pw@localhost/my_db")
my_conn = my_conn.connect() # Connection object
r_set = my_conn.execute(text('SELECT * FROM student'))
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set]
# l1=['id','Name','Class','Mark','Gender']MySQL Database
SQLite database as data source
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\sqlite\\my_db.db")
my_conn = my_conn.connect() # Connection object
r_set = my_conn.execute(text('SELECT * FROM student'))
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set]Pandas DataFrame as source
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel('D:\\student.xlsx') # Create dataframe using xlsx file
l1 = list(df) # List of column names as headers
r_set = df.to_numpy().tolist() # Create list of lists using rowsExcel file as source
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook(filename='D:\\student.xlsx', read_only=True)
ws = wb['Sheet1']
r_set = [row for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True)]
l1 = r_set.pop(0) # Collect the first row as column headers
wb.close() # Close the workbook after readingcsv file as data source
import csv
file = open('D:\\student.csv') # File object for student.csv file
csvreader = csv.reader(file)
l1 = []
l1 = next(csvreader) # Column headers as first row
r_set = [row for row in csvreader]json file as data source
import json
import urllib.request
# Fetch and parse JSON data
url = "https://www.plus2net.com/php_tutorial/student.json"
with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response:
data = json.load(response)
# Define column headers
l1 = [{"text": key.capitalize(), "stretch": True} for key in data[0].keys()]
# Define row data
r_set = [tuple(student.values()) for student in data]Integrating Tabelview with Data
This step is after collecting the data from sources ( l1 , r_set ).dv.build_table_data(l1, r_set) # adding column and row data
dv.load_table_data() # refresh the table view with data
dv.autofit_columns() # Adjust with available space
dv.autoalign_columns() # String left and Numbers to right import ttkbootstrap as ttk
from ttkbootstrap.tableview import Tableview
from ttkbootstrap.constants import *
my_w = ttk.Window()
my_w.geometry("400x300") # width and height
colors = my_w.style.colors # for using alternate colours
dv = ttk.tableview.Tableview(
master=my_w,
paginated=True,
searchable=True,
bootstyle=SUCCESS,
pagesize=10,
height=10,
stripecolor=(colors.light, None),
)
dv.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5) # Tableview is placed
# MySQL as data source
from sqlalchemy import create_engine,text # for MySql and SQLite database
"""
my_conn = create_engine("mysql+mysqldb://id:pw@localhost/my_tutorial") # update details
my_conn = my_conn.connect()
r_set = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM student ")) # Change the query
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of Column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set] # List of rows of data
"""
# SQlite database as datasource
"""
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\sqlite\\my_db.db") # Update your path
my_conn = my_conn.connect()
r_set = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM student"))
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set]
"""
# Pandas dataframe as source
"""
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel("I:\data\student.xlsx") # create dataframe using xlsx file
l1 = list(df) # List of column names as headers
r_set = df.to_numpy().tolist() # Create list of list using rows
"""
# Excel file as source
"""
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook(filename="I:\data\student.xlsx", read_only=True)
ws = wb["student"]
r_set = [row for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True)]
l1 = r_set.pop(0) # Collect the first row as column headers
wb.close() # Close the workbook after reading
"""
# CSV file as source
import csv
file = open("I:\data\student.csv") # file object for student.csv file
csvreader = csv.reader(file)
l1 = []
l1 = next(csvreader) # column headers as first row
r_set = [row for row in csvreader]
# Integrate the data source to Tableview
dv.build_table_data(l1, r_set) # adding column and row data
dv.load_table_data() # refresh the table view with data
dv.autofit_columns() # Adjust with available space
dv.autoalign_columns() # String left and Numbers to right
my_w.mainloop()
Keeping a separate Data Source file
We can keep all the data sources in a different file and use only two variables l1 and r_set. From our main file we can call these two variables like this.from ttk_table_sources import r_set, l1'''
r_set = [
[1, "John Deo", "Four", 75, "female"],
[2, "Max Ruin", "Three", 85, "male"],
[3, "Arnold", "Three", 55, "male"],
[4, "Krish Star", "Four", 60, "female"],
[5, "John Mike", "Four", 60, "female"],
[6, "Alex John", "Four", 55, "male"],
[7, "My John Rob", "Five", 78, "male"],
[8, "Asruid", "Five", 85, "male"],
[9, "Tes Qry", "Six", 78, "male"],
[10, "Big John", "Four", 55, "female"],
]
l1 = ["id", "name", "class", "mark", "gender"]
'''
# MySQL as data source
from sqlalchemy import create_engine ,text # for MySql and SQLite database
my_conn = create_engine("mysql+mysqldb://id:pw@localhost/my_tutorial")
my_conn = my_conn.connect()
r_set = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM student")) # Change the query
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of Column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set] # List of rows of data
# SQlite database as datasource
"""
my_conn = create_engine("sqlite:///D:\\testing\\sqlite\\my_db.db")
my_conn = my_conn.connect()
r_set = my_conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM student") )
l1 = [r for r in r_set.keys()] # List of column headers
r_set = [list(r) for r in r_set]
"""
# Pandas dataframe as source
"""
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel("I:\data\student.xlsx") # create dataframe using xlsx file
l1 = list(df) # List of column names as headers
r_set = df.to_numpy().tolist() # Create list of list using rows
"""
# Excel file as source
"""
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook(filename="I:\data\student.xlsx", read_only=True)
ws = wb["student"]
r_set = [row for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True)]
l1 = r_set.pop(0) # Collect the first row as column headers
wb.close() # Close the workbook after reading
"""
# CSV file as source
"""
import csv
file = open("F:\data\student.csv") # file object for student.csv file
csvreader = csv.reader(file)
l1 = []
l1 = next(csvreader) # column headers as first row
r_set = [row for row in csvreader]
"""import ttkbootstrap as ttk
from ttkbootstrap.tableview import Tableview
from ttkbootstrap.constants import *
from ttk_table_sources import r_set, l1
my_w = ttk.Window()
my_w.geometry("400x300") # width and height
colors = my_w.style.colors # for using alternate colours
dv = ttk.tableview.Tableview(
master=my_w,
paginated=True,
searchable=False,
bootstyle=SUCCESS,
pagesize=10,
height=10,
stripecolor=(colors.light, None),
)
dv.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5) # Tableview is placed
# Integrate the data source to Tableview
marks = [int(r[3]) for r in r_set] # List of all marks column
dv.build_table_data(l1, r_set) # adding column and row data
dv.insert_row("end", values=["-", "-SUM-", "All", sum(marks), "All"])
dv.insert_row("end", values=["-", "-MAX-", "All", max(marks), "All"])
dv.load_table_data() # refresh the table view with data
dv.autofit_columns() # Adjust with available space
dv.autoalign_columns() # String left and Numbers to right
my_w.mainloop()

Subhendu Mohapatra
Author
🎥 Join me live on YouTubePassionate about coding and teaching, I publish practical tutorials on PHP, Python, JavaScript, SQL, and web development. My goal is to make learning simple, engaging, and project‑oriented with real examples and source code.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel here
This article is written by plus2net.com team.
https://www.plus2net.com

 Python Video Tutorials
Python Video Tutorials